Antiamyloid Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Alzheimer Disease: Emerging Issues in Neurology
- PMID: 37495380
- PMCID: PMC10663011
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207757
Antiamyloid Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Alzheimer Disease: Emerging Issues in Neurology
Abstract
With recent data demonstrating that lecanemab treatment can slow cognitive and functional decline in early symptomatic Alzheimer disease (AD), it is widely anticipated that this drug and potentially other monoclonal antibody infusions targeting β-amyloid protein will imminently be realistic options for some patients with AD. Given that these new antiamyloid monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are associated with nontrivial risks and burdens of treatment that are radically different from current mainstays of AD management, effectively and equitably translating their use to real-world clinical care will require systematic and practice-specific modifications to existing workflows and infrastructure. In this Emerging Issues in Neurology article, we provide practical guidance for a wide audience of neurology clinicians on logistic adaptations and decision making around emerging antiamyloid mAbs. Specifically, we briefly summarize the rationale and available evidence supporting antiamyloid mAb use in AD to facilitate appropriate communication with patients and care partners on potential benefits. We also discuss pragmatic approaches to optimizing patient selection and treatment monitoring, with a particular focus on the value of incorporating shared decision making and multidisciplinary collaboration. In addition, we review some of the recognized limitations of current knowledge and highlight areas of future evolution to guide the development of sustainable and flexible models for treatment and follow-up. As the field enters a new era with disease-modifying treatment options for AD, it will be critical for neurology practices to prepare and continually innovate to ensure optimal outcomes for patients.
© 2023 American Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
V.K. Ramanan is a site clinician in the Eisai-supported AHEAD 3-45 trial which is testing lecanemab in patients with preclinical Alzheimer disease, is the co-PI for a clinical trial sponsored by the Alzheimer's Association, is a site clinician for clinical trials supported by the Alzheimer's Treatment and Research Institute at USC and Transposon Therapeutics, Inc., reports research funding from the NIH and the Mangurian Foundation for Lewy Body disease research all unrelated to this work, and has also provided educational content for Medscape. M.J. Armstrong is employed by the University of Florida; receives research support from the NIH (R01AG068128, P30AG047266, R01NS121099, R44AG062072), the Florida Department of Health (grant 20A08), and as the local PI of a Lewy Body Dementia Association Research Center of Excellence; serves on the DSMBs for the Alzheimer's Therapeutic Research Institute/Alzheimer's Clinical Trial Consortium and the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study; and has provided educational content for Medscape and Vindico. P. Choudhury reports research support from the Arizona Alzheimer's Research Consortium, is a site clinician for the Eisai-sponsored AHEAD3-45 and CLARITY-AD open-label extension trials, is a site clinician for trials supported by Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study (ADCS), Alzheimer's Treatment and Research Institute at USC, Cassava Sciences, Inc., Biogen, Cognition Therapeutics, Novo Nordisk A/S, and the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and is PI for a clinical trial sponsored by Cognito Therapeutics. K.A. Coerver receives salary support from CenExel and research support from Eli Lilly, Sage Therapeutics, Annovis, CND Life and Spark Neuro Inc., and Athira. R.H. Hamilton reports research funding from the NIH, the Department of Defense, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, and private philanthropic giving all unrelated to this work and has received funding as a speaker on topics related to diversity and inclusion by Alexion Pharmaceuticals and Starfish Neurosciences. B.C. Klein has received honoraria for speaking at American Academy of Neurology courses; serves on the speaker's bureau of Abbvie, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Impel, Theranica, and Lundbeck; has served as consultant for Abbvie, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Lundbeck, and Pfizer; has served as an advisor for Ipsen; has received (via his practice) commercial research support from Abbvie; has equity interest in Abington Neurological Associates, Ltd. and AppsByDocs, LLC, makers of p-cog; and is a member of the American Academy of Neurology Board of Directors. D.A. Wolk has received personal fees from Eli Lilly, GE Healthcare, Qynapse, and Functional Neuromodulation and grants from Biogen, the NIH, and the Alzheimer's Association outside of the submitted work. S.R. Wessels has reported no conflicts of interest. L.K. Jones serves in a voluntary capacity on boards of directors of the Mayo Clinic ACO and the American Academy of Neurology Institute and is editor-in-chief of
Figures
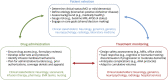

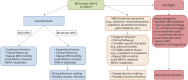
References
-
- Alzheimer's Association. Alzheimer's Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimer's Association; 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
