Effect of experimental hookworm infection on insulin resistance in people at risk of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 37495576
- PMCID: PMC10372076
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40263-4
Effect of experimental hookworm infection on insulin resistance in people at risk of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
The reduced prevalence of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in countries with endemic parasitic worm infections suggests a protective role for worms against metabolic disorders, however clinical evidence has been non-existent. This 2-year randomised, double-blinded clinical trial in Australia of hookworm infection in 40 male and female adults at risk of type 2 diabetes assessed the safety and potential metabolic benefits of treatment with either 20 (n = 14) or 40 (n = 13) Necator americanus larvae (L3) or Placebo (n = 13) (Registration ACTRN12617000818336). Primary outcome was safety defined by adverse events and completion rate. Homoeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance, fasting blood glucose and body mass were key secondary outcomes. Adverse events were more frequent in hookworm-treated participants, where 44% experienced expected gastrointestinal symptoms, but completion rates were comparable to Placebo. Fasting glucose and insulin resistance were lowered in both hookworm-treated groups at 1 year, and body mass was reduced after L3-20 treatment at 2 years. This study suggests hookworm infection is safe in people at risk of type 2 diabetes and associated with improved insulin resistance, warranting further exploration of the benefits of hookworms on metabolic health.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.R.G and A.L, are founders and shareholders of Macrobiome Therapeutics, which is developing hookworm-derived proteins as drugs for treating inflammatory conditions. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
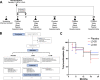
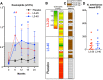
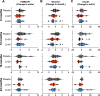
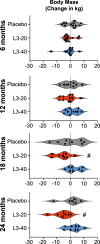
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edn 2021 https://diabetesatlas.org/ (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

