AtOM, an ontology model to standardize use of brain atlases in tools, workflows, and data infrastructures
- PMID: 37495585
- PMCID: PMC10372146
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02389-4
AtOM, an ontology model to standardize use of brain atlases in tools, workflows, and data infrastructures
Abstract
Brain atlases are important reference resources for accurate anatomical description of neuroscience data. Open access, three-dimensional atlases serve as spatial frameworks for integrating experimental data and defining regions-of-interest in analytic workflows. However, naming conventions, parcellation criteria, area definitions, and underlying mapping methodologies differ considerably between atlases and across atlas versions. This lack of standardized description impedes use of atlases in analytic tools and registration of data to different atlases. To establish a machine-readable standard for representing brain atlases, we identified four fundamental atlas elements, defined their relations, and created an ontology model. Here we present our Atlas Ontology Model (AtOM) and exemplify its use by applying it to mouse, rat, and human brain atlases. We discuss how AtOM can facilitate atlas interoperability and data integration, thereby increasing compliance with the FAIR guiding principles. AtOM provides a standardized framework for communication and use of brain atlases to create, use, and refer to specific atlas elements and versions. We argue that AtOM will accelerate analysis, sharing, and reuse of neuroscience data.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.E.M. is the founder and has equity interest in SciCrunch Inc, a tech start-up out of UCSD that provides tools and services in support of reproducible science and Research Resource Identifiers. J.G.B. is a member of the Management Board of the EBRAINS AISBL, Brussels, Belgium. The other authors declare that no competing interests or conflicts of interest exist for any of the authors.
Figures

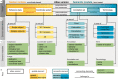

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 785907/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 945539/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 945539/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 785907/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 945539/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)

