Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces
- PMID: 37495593
- PMCID: PMC10372074
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39721-w
Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces
Abstract
Genetic analysis methods are foundational to advancing personalized medicine, accelerating disease diagnostics, and monitoring the health of organisms and ecosystems. Current nucleic acid technologies such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) rely on sample amplification and can suffer from inhibition. Here, we introduce a label-free genetic screening platform based on high quality (high-Q) factor silicon nanoantennas functionalized with nucleic acid fragments. Each high-Q nanoantenna exhibits average resonant quality factors of 2,200 in physiological buffer. We quantitatively detect two gene fragments, SARS-CoV-2 envelope (E) and open reading frame 1b (ORF1b), with high-specificity via DNA hybridization. We also demonstrate femtomolar sensitivity in buffer and nanomolar sensitivity in spiked nasopharyngeal eluates within 5 minutes. Nanoantennas are patterned at densities of 160,000 devices per cm2, enabling future work on highly-multiplexed detection. Combined with advances in complex sample processing, our work provides a foundation for rapid, compact, and amplification-free molecular assays.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
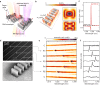
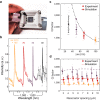
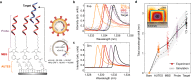
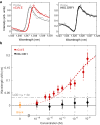
Update of
-
Rapid genetic screening with high quality factor metasurfaces.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2021 Oct 15:arXiv:2110.07862v2. ArXiv. 2021. Update in: Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 26;14(1):4486. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39721-w. PMID: 34671699 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Zhang, Y. et al. A system of coordinated autonomous robots for lagrangian studies of microbes in the oceanic deep chlorophyll maximum. Sci. Robotics6 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

