Impact of analysis of the sentinel lymph node by one-step nucleic acid amplification (OSNA) compared to conventional histopathology on axillary and systemic treatment: data from the Dutch nationwide cohort of breast cancer patients
- PMID: 37495799
- PMCID: PMC10505596
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-023-07065-0
Impact of analysis of the sentinel lymph node by one-step nucleic acid amplification (OSNA) compared to conventional histopathology on axillary and systemic treatment: data from the Dutch nationwide cohort of breast cancer patients
Abstract
Purpose: The outcome of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer patients affects adjuvant treatment. Compared to conventional histopathology, analysis by one-step nucleic acid amplification (OSNA) harvests more micrometastasis, potentially inducing overtreatment. In this study we investigated the impact of OSNA analysis on adjuvant treatment, compared to histopathological analysis.
Methods: Data from T1-3 breast cancer patients with sentinel nodes analysed between January 2016 and December 2019 by OSNA (OSNA group, n = 1086) from Zuyderland Medical Centre, the Netherlands, were compared to concurrent data from the Netherlands Cancer Registry (NKR) where sentinel nodes were examined by histology (histology group, n = 35,143). Primary outcomes were micro- or macrometastasis, axillary treatments (axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) or axillary radiotherapy (ART)), chemotherapy, and endocrine therapy. Statistics with Pearson Chi-square.
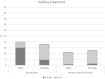
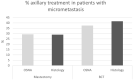
Results: In the OSNA group more micrometastasis (14.9%) were detected compared to the histology group (7.9%, p < 0.001). No difference in axillary treatment between groups was detected (14.3 vs. 14.4%). In case of mastectomy and macrometastasis, ALND was preferred over ART in the OSNA group (14.9%) compared to the histology group (4.4%, p < 0.001). In cases of micrometastasis, no difference was seen. There was no difference in administration of adjuvant chemotherapy between groups. Endocrine treatment was administrated less often in the OSNA group compared to the histology group (45.8% vs. 50.8%, p < 0.002).
Conclusion: More micrometastasis were detected by OSNA compared to histopathology, but no subsequent increase in adjuvant axillary and systematic treatment was noticed. When performing mastectomy and OSNA, there was a preference for ALND compared to ART.
Keywords: Adjuvant treatment; Breast cancer; One-step nucleic acid amplification; Sentinel lymph node biopsy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical