Massage protects skeletal muscle from injury during long-term heavy-duty exercise via integrin β1 and laminin 2 channels of basement membrane
- PMID: 37495963
- PMCID: PMC10369692
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-04094-6
Massage protects skeletal muscle from injury during long-term heavy-duty exercise via integrin β1 and laminin 2 channels of basement membrane
Abstract
Background: Massage is widely used in exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage (EIMD). It has been proven that massage can improve the morphology and function of damaged skeletal muscle in multiple ways. However, whether massage can protect skeletal muscles from injury during long-term heavy-duty exercise has not yet been determined.
Methods: In this study, a rat model of overuse injury was established by eccentric running for 4 weeks, and pressing at constant pressure and frequency and massage were used as intervention methods to explore whether massage could protect skeletal muscle from injury through upregulating integrin and the basement membrane laminin.
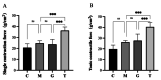
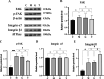
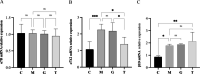
Results: The results showed that compared with the model group, the ultrastructure of skeletal muscle in the massage group was relatively complete and clear, and the maximum isotonic and tetanic contraction forces were significantly increased (P < 0.01). In addition, in the massage group, β1 integrin expression was significantly increased, p-FAK protein expression was decreased, and the co-localization of β1 integrin and the basement membrane laminin 2 was significantly increased (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Our study shows that during long-term heavy-duty exercise, massage can enhance the cell adhesion function mediated by integrin β1 and laminin 2 to protect skeletal muscle from injury and prevent the occurrence of overuse injury.
Keywords: Laminin 2; Long-term heavy exercise; Massage; Overuse injury; Skeletal muscle; α7β1 integrin.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests regarding the publication of this manuscript to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vipera lebetina venom contains two disintegrins inhibiting laminin-binding beta1 integrins.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 18;278(29):26488-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301860200. Epub 2003 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12719418
-
β1D chain increases α7β1 integrin and laminin and protects against sarcolemmal damage in mdx mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Apr 1;21(7):1592-603. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr596. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 22180459 Free PMC article.
-
Division of labor among the alpha6beta4 integrin, beta1 integrins, and an E3 laminin receptor to signal morphogenesis and beta-casein expression in mammary epithelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Sep;10(9):2817-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.9.2817. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10473629 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin signaling: linking mechanical stimulation to skeletal muscle hypertrophy.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):C629-C641. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00009.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31314586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cells, angiogenesis and muscle healing: a potential role in massage therapies?Br J Sports Med. 2013 Jun;47(9):556-60. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091685. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Br J Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23197410 Review.
Cited by
-
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Assessment of the Clinical Efficacy of the Combination of Acupressure and "Three Methods of Neck Movement (TCM)" Therapy in the Treatment of Cervical Spondylosis: A Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.J Pain Res. 2024 Nov 8;17:3651-3665. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S469511. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39534754 Free PMC article.
-
Hidden pathway: the role of extracellular matrix in type 2 diabetes mellitus-related sarcopenia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 16;16:1560396. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1560396. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40309438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xuelin RW, Zhang X, Gao J, Shi J, Li Y, Zhou The mechanism of Eccentric Exercise–induced skeletal muscle overuse injuries. Chin J Sports Med. 2012;31(12):1064–74.
-
- Crane JD et al. “Massage therapy attenuates inflammatory signaling after exercise-induced muscle damage.,” Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(119):119ra13. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002882. - PubMed
-
- Naderi A, Aminian-Far A, Gholami F, Mousavi SH, Saghari M, Howatson G. “Massage enhances recovery following exercise‐induced muscle damage in older adults,” Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports. 2021;31(3):623–632. 10.1111/sms.13883. - PubMed
-
- Boppart MD, Burkin DJ, Kaufman SJ. “α 7 β 1 -Integrin regulates mechanotransduction and prevents skeletal muscle injury,” American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2006;290(6):C1660–C1665. 10.1152/ajpcell.00317.2005. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

