A novel strategy for L-arginine production in engineered Escherichia coli
- PMID: 37495979
- PMCID: PMC10373293
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-023-02145-8
A novel strategy for L-arginine production in engineered Escherichia coli
Erratum in
-
Correction: A novel strategy for L-arginine production in engineered Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Feb 10;23(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02328-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 38341602 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: L-arginine is an important amino acid with applications in diverse industrial and pharmaceutical fields. N-acetylglutamate, synthesized from L-glutamate and acetyl-CoA, is a precursor of the L-arginine biosynthetic branch in microorganisms. The enzyme that produces N-acetylglutamate, N-acetylglutamate synthase, is allosterically inhibited by L-arginine. L-glutamate, as a central metabolite, provides carbon backbone for diverse biological compounds besides L-arginine. When glucose is the sole carbon source, the theoretical maximum carbon yield towards L-arginine is 96.7%, but the experimental highest yield was 51%. The gap of L-arginine yield indicates the regulation complexity of carbon flux and energy during the L-arginine biosynthesis. Besides endogenous biosynthesis, N-acetylglutamate, the key precursor of L-arginine, can be obtained by chemical acylation of L-glutamate with a high yield of 98%. To achieve high-yield production of L-arginine, we demonstrated a novel approach by directly feeding precursor N-acetylglutamate to engineered Escherichia coli.
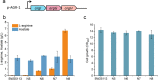
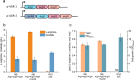
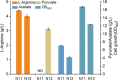
Results: We reported a new approach for the high yield of L-arginine production in E. coli. Gene argA encoding N-acetylglutamate synthase was deleted to disable endogenous biosynthesis of N-acetylglutamate. The feasibility of external N-acetylglutamate towards L-arginine was verified via growth assay in argA- strain. To improve L-arginine production, astA encoding arginine N-succinyltransferase, speF encoding ornithine decarboxylase, speB encoding agmatinase, and argR encoding an arginine responsive repressor protein were disrupted. Based on overexpression of argDGI, argCBH operons, encoding enzymes of the L-arginine biosynthetic pathway, ~ 4 g/L L-arginine was produced in shake flask fermentation, resulting in a yield of 0.99 mol L-arginine/mol N-acetylglutamate. This strain was further engineered for the co-production of L-arginine and pyruvate by removing genes adhE, ldhA, poxB, pflB, and aceE, encoding enzymes involved in the conversion and degradation of pyruvate. The resulting strain was shown to produce 4 g/L L-arginine and 11.3 g/L pyruvate in shake flask fermentation.
Conclusions: Here, we developed a novel approach to avoid the strict regulation of L-arginine on ArgA and overcome the metabolism complexity in the L-arginine biosynthesis pathway. We achieve a high yield of L-arginine production from N-acetylglutamate in E. coli. Co-production pyruvate and L-arginine was used as an example to increase the utilization of input carbon sources.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; L-Arginine; Metabolic engineering; N-acetylglutamate.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
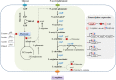
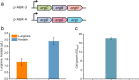
 indicate the deletion of the relevant genes. Black thick arrows indicate increased fluxes by directly overexpressing the corresponding genes. Black dashes indicate the negative feedback inhibition mechanisms. The role of ArgR repressor regulation on
indicate the deletion of the relevant genes. Black thick arrows indicate increased fluxes by directly overexpressing the corresponding genes. Black dashes indicate the negative feedback inhibition mechanisms. The role of ArgR repressor regulation on 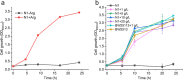
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

