A Review of Existing and New Treatments for the Management of Hand Eczema
- PMID: 37496489
- PMCID: PMC10617006
- DOI: 10.1177/12034754231188325
A Review of Existing and New Treatments for the Management of Hand Eczema
Abstract
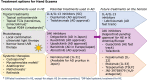
Hand eczema is a chronic condition that affects an estimated 14.5% of the general population. It has severe quality of life ramifications in those that struggle with it, including days missed from work or school, productivity loss and impaired work functioning. For years, the standard of care included topical moisturizing creams, topical steroids and more recently systemic agents. As new therapeutic targets emerge and recent advances are being developed, it is now more possible than ever that hand eczema can be managed via the underlying mechanisms. A review of the literature was conducted to identify current treatment options for hand eczema and chronic hand eczema. The terms 'hand eczema', 'hand dermatitis' were used to search PubMed, CENTRAL and Embase. To identify new therapies still undergoing investigation, we used the terms 'hand eczema', 'hand dermatitis', 'atopic dermatitis', and 'vesicular eczema of hands and/or feet' to search Clinicaltrials.gov for all studies until December 2022. There were 56 ongoing clinical trials identified for pharmacological treatments for hand eczema on Clinicaltrials.gov from 2000 - 2022, with 16 that are new or ongoing. These included studies for dupilumab, ruxolitinib, delgocitinib (LEO124249), gusacitinib (ASN002), AFX 5931, and roflumilast (ARQ-252). Two major classes of drugs emerging for the treatment of hand eczema include IL-4/IL-13 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors. With the increase in efficacy seen with these new drugs, we are also noting improved adverse effect profiles, making them attractive options to add to a clinician's management toolbox for patients with hand eczema.
Keywords: dermatology; hand dermatitis; hand eczema; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: JSSH reports no conflicts of interest. SM has received consultation and speaker honoraria from Abbvie, Basilea, Evidera, GSK, LEO Pharma, Lilly, Pfizer, and is a current study investigator for LEO Pharma and Novartis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials