Ca-EDTA restores the activity of ceftazidime-avibactam or aztreonam against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiellapneumoniae infections
- PMID: 37496674
- PMCID: PMC10366478
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107215
Ca-EDTA restores the activity of ceftazidime-avibactam or aztreonam against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiellapneumoniae infections
Abstract
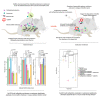
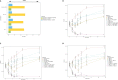
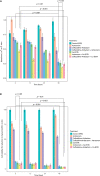
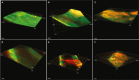
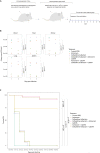
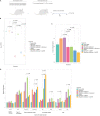
Developing an effective therapy to overcome carbapenemase-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae (CPKp) is an important therapeutic challenge that must be addressed urgently. Here, we explored a Ca-EDTA combination with aztreonam or ceftazidime-avibactam in vitro and in vivo against diverse CPKp clinical isolates. The synergy testing of this study demonstrated that novel aztreonam-Ca-EDTA or ceftazidime-avibactam-Ca-EDTA combination was significantly effective in eliminating planktonic and mature biofilms in vitro, as well as eradicating CPKp infections in vivo. Both combinations revealed significant therapeutic efficacies in reducing bacterial load in internal organs and protecting treated mice from mortality. Conclusively, this is the first in vitro and in vivo study to demonstrate that novel aztreonam-Ca-EDTA or ceftazidime-avibactam-Ca-EDTA combinations provide favorable efficacy and safety for successful eradication of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae planktonic and biofilm infections.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Health sciences; Immunology; Medical microbiology; Medical specialty; Medicine; Microbiology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo bactericidal activity of ceftazidime-avibactam against Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018 Nov 21;7:142. doi: 10.1186/s13756-018-0435-9. eCollection 2018. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018. PMID: 30479755 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antibacterial activity of ceftazidime/avibactam in combination against planktonic and biofilm carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from blood.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020 Dec;23:4-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2020.07.028. Epub 2020 Aug 15. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020. PMID: 32810638
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations of β-Lactam/β-Lactamase Mono- and Combined Therapies against Carbapenem-Nonsusceptible Enterobacteriaceae in Taiwan.Microorganisms. 2020 Dec 12;8(12):1981. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121981. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33322803 Free PMC article.
-
Carbapenemase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: implication on future therapeutic strategies.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022 Jan;20(1):53-69. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2021.1935237. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022. PMID: 34033499 Review.
-
Ceftazidime-Avibactam: A Novel Cephalosporin/β-Lactamase Inhibitor Combination for the Treatment of Resistant Gram-negative Organisms.Clin Ther. 2016 Mar;38(3):431-44. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Clin Ther. 2016. PMID: 26948862 Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection and Drug Resistance in 17 Pediatric Intensive Care Units in China from 2016 to 2022.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Sep 23;17:4125-4136. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S475720. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39351447 Free PMC article.
-
tesG expression as a potential clinical biomarker for chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pulmonary biofilm infections.BMC Med. 2025 Mar 31;23(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-04009-x. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40165235 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory carriage of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae by indigenous populations of Malaysia.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 17;25(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10276-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38632538 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Ceftazidime-Avibactam in the Treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection: A Retrospective Analysis from a Hospital in China.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Nov 14;16:7227-7237. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S435882. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 38023408 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of aloe emodin, emodin, and rhein from Aloe with EDTA sensitizes the resistant Acinetobacter baumannii to polymyxins.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 13;14:1467607. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1467607. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39346899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okanda T., Haque A., Koshikawa T., Islam A., Huda Q., Takemura H., Matsumoto T., Nakamura S. Characteristics of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated in the Intensive Care Unit of the Largest Tertiary Hospital in Bangladesh. Front. Microbiol. 2020;11:612020. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.612020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

