Central nervous system-related safety and tolerability of add-on ketamine to standard of care treatment in treatment-resistant psychotic depression in patients with major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder
- PMID: 37496742
- PMCID: PMC10366536
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1214972
Central nervous system-related safety and tolerability of add-on ketamine to standard of care treatment in treatment-resistant psychotic depression in patients with major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder
Abstract
Background: Psychotic treatment-resistant depression represents a complex and challenging form of mood disorder in clinical practice. Despite its severity, psychotic depression is frequently underdiagnosed and inadequately treated. Ketamine has demonstrated rapid and potent antidepressant effects in clinical studies, while exhibiting a favorable safety and tolerability profile. Although there is limited literature available on the use of ketamine in psychotic TRD, reports on its efficacy, safety, and tolerability profile are of great interest to clinicians. The aim of this study is to investigate the relationship between dissociative symptomatology and psychomimetic effects in inpatients with treatment-resistant major psychotic depression and treatment-resistant bipolar psychotic depression, who receive intravenous ketamine treatment alongside psychotropic medication, both during and after treatment.
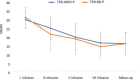
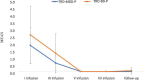
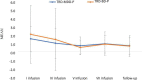
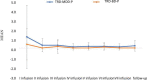
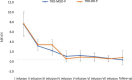
Materials and methods: A total of 36 patients diagnosed with treatment-resistant unipolar (17 patients) or bipolar (18 patients) depression with psychotic features were treated with eight intravenous infusions of 0.5 mg/kg ketamine twice a week over 4 weeks. Ketamine was given in addition to their standard of care treatment. The severity of depressive symptoms was evaluated using the MADRS, while dissociative and psychomimetic symptoms were assessed using the CADSS and BPRS, respectively.
Results: There were no statistically significant changes observed in MADRS, CADSS, and BPRS scores within the study group during ketamine infusions. However, significant improvements in MADRS, CADSS, and BPRS scores were observed during ketamine infusions in both the unipolar and bipolar depression groups.
Conclusion: This study provides support for the lack of exacerbation of psychotic symptoms in both unipolar and bipolar depression.
Keywords: bipolar depression; dissociation; ketamine; psychotic depression; treatment-resistant depression.
Copyright © 2023 Gałuszko-Wȩgielnik, Jakuszkowiak-Wojten, Wiglusz, Cubała and Pastuszak.
Conflict of interest statement
WC has received Grants: Acadia, Alkermes, Allergan, Angelini, Auspex Pharmaceuticals, BMS, Celon, Cephalon, Cortexyme, Ferrier, Forest Laboratories, GedeonRichter, GWPharmaceuticals, HMNC Brain Health, IntraCellular Therapies, Janssen, KCR, Lilly, Lundbeck, Minerva, MSD, NIH, Novartis, Orion, Otsuka, Sanofi, Servier. Honoraria: Adamed, Angelini, AstraZeneca, BMS, Celon, GSK, Janssen, KRKA, Lekam, Lundbeck, Minerva, NeuroCog, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, Polfa Tarchomin, Sanofi, Servier, Zentiva. Advisory boards: Angelini, Celon (terminated), Douglas Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Sanofi; MG-W has received research support from Alkermes, Biogen, Celon, Janssen, KCR, Minerva Neurosciences, Lilly, and Servier, Novartis; KJ-W has received research support from Alkermes, Auspex, Biogen, Celon, Gedeon-Richter, GW Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, KCR, Lilly, Lundbeck, Minerva Neurosciences, Orion, Otsuka, and Servier; MW has received research support from Alkermes, Auspex Pharmaceuticals, Biogen, Cephalon, Celon, Cortexyme, Eli Lilly, Ferrier, Forest Laboratories, GedeonRichter, GWPharmaceuticals, Janssen, Lundbeck, Orion, Otsuka, and Servier; Speakers bureau: Lundbeck, Servier. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Beck K., Hindley G., Borgan F., Ginestet C., McCutcheon R., Brugger S., et al. (2020). Association of ketamine with psychiatric symptoms and implications for its therapeutic use and for understanding schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 3:e204693. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.4693 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

