Analysis of the efficacy of abdominal massage on functional constipation: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 37496907
- PMCID: PMC10366436
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18098
Analysis of the efficacy of abdominal massage on functional constipation: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Constipation is a digestive disorder with a high global prevalence, with approximately 20-25% of the population suffering from constipation, and the majority of constipated patients experience functional constipation (FC). Although abdominal massage is an effective intervention, there is a lack of analysis of the efficacy of abdominal massage in the treatment of functional constipation. Objective: To evaluate the clinical efficacy of abdominal massage in the treatment of functional constipation.
Methods: A computerized retrieval of randomized controlled trials on abdominal massage for functional constipation was conducted on China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang, VIP Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database, Chinese BioMedical Literature Database, Cochrane Database, PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science until October 1, 2022. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software after the initial screening and re-screening of the literature.
Results: A total of 13 papers involving 830 patients were included. The results of the meta-analysis showed that abdominal massage had better efficacy in the treatment of functional constipation. Constipated patients in the treatment group showed greater improvement in the frequency of defecation, difficulty in defecation, stool properties, and PAC-QOL scores than those in the control group. The SMD/MD values and 95% CI of each score were: SMD = 1.05, 95%CI (0.63,1.46); SMD = -1.51, 95%CI (-2.35,-0.68); SMD = 0.95, 95%CI (0.31,1.59); MD = -13.24, 95%CI (-25.83, -0.65).
Conclusion: Abdominal massage can increase the frequency of defecation, reduce the symptoms of difficulty in defecation, improve stool properties, and positively affect the quality of life of patients with constipation. Hence, abdominal massage therapy shows definite therapeutic efficacy for functional constipation, providing a more specific plan for clinical treatment.
Keywords: Abdominal massage; Functional constipation; Meta-analysis; Other therapies.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




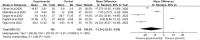











References
-
- Wang F., Sun S., Yin Z., et al. Acupuncture point patching for functional constipation: digging into the rules of acupuncture point selection and medication use. Chinese Acupunc. 2021;41:5. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20200823-k0003. - DOI
-
- Li J., Chen J., Ke X. Consensus opinion on the combined diagnosis and treatment of functional constipation in Chinese and Western medicine. Chinese J. Integrat. Gastroenterol. 2017;26(2018):9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2018.01.03. - DOI
-
- Zhang B., Wei A., Chen X., et al. Investigation of the relationship between constipation and Alzheimer's disease. Chinese J. Gerontol. 2009;29:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2009.22.043. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

