A survey of the specificity and mechanism of 1,6 hexanediol-induced disruption of nuclear transport
- PMID: 37498221
- PMCID: PMC10376917
- DOI: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2240139
A survey of the specificity and mechanism of 1,6 hexanediol-induced disruption of nuclear transport
Abstract
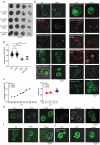
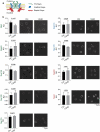
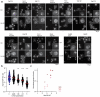
Selective transport through the nuclear pore complex (NPC) depends on the dynamic binding of FG-repeat containing nucleoporins, the FG-nups, with each other and with Karyopherins (Kaps). Here, we assessed the specificity and mechanism by which the aliphatic alcohol 1,6-hexanediol (1,6HD) disrupts the permeability barrier of NPCs in live baker's yeast cells. After a 10-minute exposure to 5% 1,6HD, no notable changes were observed in cell growth, cytosolic pH and ATP levels, or the appearance of organelles. However, effects on the cytoskeleton and Hsp104 were noted. 1,6HD clearly affected the NPC permeability barrier, allowing passive nuclear entry of a 177kDa reporter protein that is normally confined to the cytosol. Moreover, multiple Kaps were displaced from NPCs, and the displacement of Kap122-GFP correlated with the observed passive permeability changes. 1,6HD thus temporarily permeates NPCs, and in line with Kap-centric models, the mechanism includes the release of numerous Kaps from the NPCs.
Keywords: 1,6-hexanediol; Karyopherin; Nuclear pore complex; Nuclear transport receptors; aliphatic alcohol; baker’s yeast; liquid-liquid phase separation; nuclear transport.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s). The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
