Identification of variants in genes associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Mexican patients
- PMID: 37498360
- PMCID: PMC10657276
- DOI: 10.1007/s00438-023-02048-8
Identification of variants in genes associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Mexican patients
Erratum in
-
Correction: Identification of variants in genes associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in Mexican patients.Mol Genet Genomics. 2023 Nov;298(6):1593. doi: 10.1007/s00438-023-02069-3. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Mol Genet Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37861817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
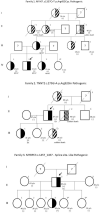
The objective of this work was to identify genetic variants in Mexican patients diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). According to world literature, the genes mainly involved are MHY7 and MYBPC3, although variants have been found in more than 50 genes related to heart disease and sudden death, and to our knowledge there are no studies in the Mexican population. These variants are reported and classified in the ClinVar (PubMed) database and only some of them are recognized in the Online Mendelian Information in Men (OMIM). The present study included 37 patients, with 14 sporadic cases and 6 familial cases, with a total of 21 index cases. Next-generation sequencing was performed on a predesigned panel of 168 genes associated with heart disease and sudden death. The sequencing analysis revealed twelve (57%) pathogenic or probably pathogenic variants, 9 of them were familial cases, managing to identify pathogenic variants in relatives without symptoms of the disease. At the molecular level, nine of the 12 variants (75%) were single nucleotide changes, 2 (17%) deletions, and 1 (8%) splice site alteration. The genes involved were MYH7 (25%), MYBPC3 (25%) and ACADVL, KCNE1, TNNI3, TPM1, SLC22A5, TNNT2 (8%). In conclusion; we found five variants that were not previously reported in public databases. It is important to follow up on the reclassification of variants, especially those of uncertain significance in patients with symptoms of the condition. All patients included in the study and their relatives received family genetic counseling.
Keywords: Gene variants; Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; MYBPC3; MYH7; Sudden death.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of variants in MYH7, MYBPC3 and TNNT2 with sudden cardiac death-related risk factors in Brazilian patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2021 May;52:102478. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2021.102478. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2021. PMID: 33588347
-
Somatic MYH7, MYBPC3, TPM1, TNNT2 and TNNI3 mutations in sporadic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Circ J. 2013;77(9):2358-65. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-13-0294. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Circ J. 2013. PMID: 23782526 Clinical Trial.
-
Spectrum of Mutations in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Genes Among Tunisian Patients.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016 Nov;20(11):674-679. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2016.0187. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016. PMID: 27574918
-
Sarcomeric gene variants among Indians with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A scoping review.Indian J Med Res. 2023 Aug;158(2):119-135. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_3567_21. Indian J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37787257 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes associated with sarcomere mutations in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a meta-analysis on 7675 individuals.Clin Res Cardiol. 2018 Jan;107(1):30-41. doi: 10.1007/s00392-017-1155-5. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Clin Res Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 28840316 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a novel likely pathogenic TPM1 variant linked to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a family with sudden cardiac death.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Oct;11(5):3180-3190. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14906. Epub 2024 Jun 14. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38874371 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pathogenic variant in the carnitine transporter gene, SLC22A5, in association with metabolic carnitine deficiency and cardiomyopathy features.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03676-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38166572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alyousfi D, Baralle D, Collins A. Essentiality-specific pathogenicity prioritization gene score to improve filtering of disease sequence data. Brief Bioinform. 2021;22(2):1782–1789. - PubMed
-
- Anan R, Shono H, Kisanuki A, Arima S, Nakao S, Tanaka H. Patients with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by a Phe110Ile missense mutation in the cardiac troponin T gene have variable cardiac morphologies and a favorable prognosis. Circulation. 1998;98(5):391–397. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous