Deregulation of exosomal miRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 37498970
- PMCID: PMC10374114
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289301
Deregulation of exosomal miRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
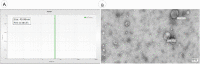
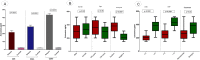
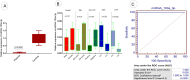
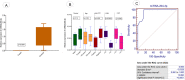
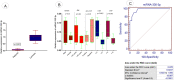
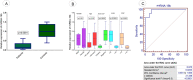
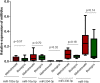
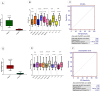
Exosomes are small-diameter endosomal vesicles secreted in all biological fluids and play biological/pathological roles in the cell. These pathological roles are played by exosome's cargo molecules through inter-cellular communication. Exosomal cargo molecules contain proteins and miRNAs. miRNAs are small non-coding RNA fragments involved in the reduction of final protein output by destabilizing or suppressing the translation of target messenger RNA (mRNA). This deregulation of the protein due to miRNAs ultimately accelerates the process of disease pathogenesis. The role of exosomal miRNAs has been investigated in different diseases and the limited number of studies have been published concerning exosomal miRNAs and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The current study is designed to investigate the role of exosomal miRNAs (miRNA-103a-3p, miRNA-10a-5p, miRNA-204-3p, miRNA-330-3p, and miRNA-19b) in the pathogenesis of RA. Furthermore, the role of selected exosomal miRNAs in RA pathogenesis was further explored by estimating oxidative stress and histone deacetylation in RA patients. In the current study, 306 RA patients and equal numbers of age/gender-matched controls were used. The level of expression of above-mentioned exosomal miRNAs was assessed by performing qRT PCR. Deacetylation and oxidative stress assays were performed to estimate the 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG level) and histone deacetylation levels using the Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Statistical analysis indicated a significantly downregulated expression of miRNA-103a-3p (p<0.0001), miR-10a-5p (p<0.0001), miR-204-3p (p<0.0001), miR-330-3p (p<0.0001) and miR-19b (p<0.0001) in RA patients compared to controls. Significantly increased levels of 8-OHdG (p<0.0001) and histone deacetylation (p<0.0001) were observed among RA patients compared to controls. Spearman correlation showed a negative correlation between the deregulated exosomal miRNAs and increased oxidative stress and histone deacetylation in RA patients. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis showed a good diagnostic specificity/sensitivity of the above-mentioned exosomal miRNAs among RA patients. These analyses indicated the potential role of deregulated exosomal miRNAs in the initiation of RA by targeting oxidative stress and histone deacetylation processes.
Copyright: © 2023 Hussain et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exosomal miRNAs involvement in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 15;11(2):e41983. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41983. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39897907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of serum exosomal miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis of Rheumatoid arthritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Mar 10;129:111604. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111604. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38320350
-
Differential Expression Profiles of Plasma Exosomal microRNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Aug 28;16:3687-3698. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S413994. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37663759 Free PMC article.
-
Whole blood microRNA expression pattern differentiates patients with rheumatoid arthritis, their seropositive first-degree relatives, and healthy unrelated control subjects.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Nov 10;19(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1459-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29126434 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal Osteoclast-Derived miRNA in Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Their Pathogenesis in Bone Erosion to New Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1506. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031506. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes in Autoimmune Diseases: A Review of Mechanisms and Diagnostic Applications.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025 Jan 17;68(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-09013-2. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39820756 Review.
-
Deregulation of Exosomal miR-17, miR-20a and TGFBR2 in Head and Neck Cancer Patients.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15330338251323314. doi: 10.1177/15330338251323314. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 39989256 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Epigenetic Regulators of Redox Homeostasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Apr 29;14(5):532. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050532. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal miRNAs involvement in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 15;11(2):e41983. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41983. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39897907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

