Preemptive immune globulin therapy in sensitized lung transplant recipients
- PMID: 37499884
- PMCID: PMC10631014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trim.2023.101904
Preemptive immune globulin therapy in sensitized lung transplant recipients
Abstract
Background: Sensitized lung transplant recipients are at increased risk of developing donor-specific antibodies, which have been associated with acute and chronic rejection. Perioperative intravenous immune globulin has been used in sensitized individuals to down-regulate antibody production.
Methods: We compared patients with a pre-transplant calculated panel reactive antibody ≥25% who did not receive preemptive immune globulin therapy to a historical control that received preemptive immune globulin therapy. Our cohort included 59 patients, 17 patients did not receive immune globulin therapy and 42 patients received therapy.
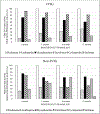
Results: Donor specific antibody development was numerically higher in the non-immune globulin group compared to the immune globulin group (58.8% vs 33.3%, respectively, odds ratio 2.80, 95% confidence interval [0.77, 10.79], p = 0.13). Median time to antibody development was 9 days (Q1, Q3: 7, 19) and 28 days (Q1, Q3: 7, 58) in the non-immune globulin and immune globulin groups, respectively. There was no significant difference between groups in the incidence of primary graft dysfunction at 72 h post-transplant or acute cellular rejection, antibody-mediated rejection, and chronic lung allograft dysfunction at 12 months.
Conclusion: These findings are hypothesis generating and emphasize the need for larger, randomized studies to determine association of immune globulin therapy with clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Donor specific antibody; Immune globulin; Transplant.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest none.
Figures

References
-
- Kransdorf EP, Pando MJ, Gragert L, Kaplan B. HLA Population Genetics in Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplantation. 2017. Sep;101(9):1971–1976. - PubMed
-
- Palmer SM, Davis RD, Hadjiliadis D, et al. Development of an antibody specific to major histocompatibility antigens detectable by flow cytometry after lung transplant is associated with bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Transplantation. 2002. Sep 27;74(6):799–804. - PubMed
-
- Le Pavec J, Suberbielle C, Lamrani L, et al. De-novo donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies 30 days after lung transplantation are associated with a worse outcome. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016. Sep;35(9):1067–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

