Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features and Tumor-to-Nipple Distance for the Nipple-Areolar Complex Involvement of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37500575
- PMCID: PMC10400374
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2022.0846
Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features and Tumor-to-Nipple Distance for the Nipple-Areolar Complex Involvement of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the accuracy of preoperative breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features and tumor-to-nipple distance (TND) for diagnosing occult nipple-areolar complex (NAC) involvement in breast cancer.
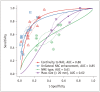
Materials and methods: The MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane databases were searched for articles published until March 20, 2022, excluding studies of patients with clinically evident NAC involvement or those treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Study quality was assessed using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 tool. Two reviewers independently evaluated studies that reported the diagnostic performance of MRI imaging features such as continuity to the NAC, unilateral NAC enhancement, non-mass enhancement (NME) type, mass size (> 20 mm), and TND. Summary estimates of the sensitivity and specificity curves and the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve of the MRI features for NAC involvement were calculated using random-effects models. We also calculated the TND cutoffs required to achieve predetermined specificity values.
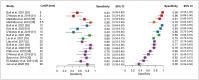
Results: Fifteen studies (n = 4002 breast lesions) were analyzed. The pooled sensitivity and specificity (with 95% confidence intervals) for NAC involvement diagnosis were 71% (58-81) and 94% (91-96), respectively, for continuity to the NAC; 58% (45-70) and 97% (95-99), respectively, for unilateral NAC enhancement; 55% (46-64) and 83% (75-88), respectively, for NME type; and 88% (68-96) and 58% (40-75), respectively, for mass size (> 20 mm). TND had an area under the SROC curve of 0.799 for NAC involvement. A TND of 11.5 mm achieved a predetermined specificity of 85% with a sensitivity of 64%, and a TND of 12.3 mm yielded a predetermined specificity of 83% with a sensitivity of 65%.
Conclusion: Continuity to the NAC and unilateral NAC enhancement may help predict occult NAC involvement in breast cancer. To achieve the desired diagnostic performance with TND, a suitable cutoff value should be considered.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Diagnostic performance; Magnetic resonance imaging; Nipple sparing mastectomy; Nipple-areolar complex.
Copyright © 2023 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Smith BL, Tang R, Rai U, Plichta JK, Colwell AS, Gadd MA, et al. Oncologic safety of nipple-sparing mastectomy in women with breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;225:361–365. - PubMed
-
- Petit JY, Veronesi U, Orecchia R, Curigliano G, Rey PC, Botteri E, et al. Risk factors associated with recurrence after nipple-sparing mastectomy for invasive and intraepithelial neoplasia. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:2053–2058. - PubMed
-
- Chan SE, Liao CY, Wang TY, Chen ST, Chen DR, Lin YJ, et al. The diagnostic utility of preoperative breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and/or intraoperative sub-nipple biopsy in nipple-sparing mastectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017;43:76–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

