Generative Adversarial Network-Based Image Conversion Among Different Computed Tomography Protocols and Vendors: Effects on Accuracy and Variability in Quantifying Regional Disease Patterns of Interstitial Lung Disease
- PMID: 37500581
- PMCID: PMC10400368
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2023.0088
Generative Adversarial Network-Based Image Conversion Among Different Computed Tomography Protocols and Vendors: Effects on Accuracy and Variability in Quantifying Regional Disease Patterns of Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
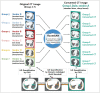
Objective: To assess whether computed tomography (CT) conversion across different scan parameters and manufacturers using a routable generative adversarial network (RouteGAN) can improve the accuracy and variability in quantifying interstitial lung disease (ILD) using a deep learning-based automated software.
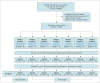
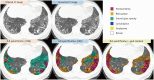
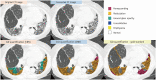
Materials and methods: This study included patients with ILD who underwent thin-section CT. Unmatched CT images obtained using scanners from four manufacturers (vendors A-D), standard- or low-radiation doses, and sharp or medium kernels were classified into groups 1-7 according to acquisition conditions. CT images in groups 2-7 were converted into the target CT style (Group 1: vendor A, standard dose, and sharp kernel) using a RouteGAN. ILD was quantified on original and converted CT images using a deep learning-based software (Aview, Coreline Soft). The accuracy of quantification was analyzed using the dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and pixel-wise overlap accuracy metrics against manual quantification by a radiologist. Five radiologists evaluated quantification accuracy using a 10-point visual scoring system.
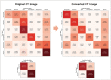
Results: Three hundred and fifty CT slices from 150 patients (mean age: 67.6 ± 10.7 years; 56 females) were included. The overlap accuracies for quantifying total abnormalities in groups 2-7 improved after CT conversion (original vs. converted: 0.63 vs. 0.68 for DSC, 0.66 vs. 0.70 for pixel-wise recall, and 0.68 vs. 0.73 for pixel-wise precision; P < 0.002 for all). The DSCs of fibrosis score, honeycombing, and reticulation significantly increased after CT conversion (0.32 vs. 0.64, 0.19 vs. 0.47, and 0.23 vs. 0.54, P < 0.002 for all), whereas those of ground-glass opacity, consolidation, and emphysema did not change significantly or decreased slightly. The radiologists' scores were significantly higher (P < 0.001) and less variable on converted CT.
Conclusion: CT conversion using a RouteGAN can improve the accuracy and variability of CT images obtained using different scan parameters and manufacturers in deep learning-based quantification of ILD.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Computed tomography; Interstitial lung disease; Quantification.
Copyright © 2023 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Joon Beom Seo, Namkug Kim, and Ho Yun Lee, contributing editors of the
Figures
References
-
- Gay SE, Kazerooni EA, Toews GB, Lynch JP, 3rd, Gross BH, Cascade PN, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: predicting response to therapy and survival. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(4 Pt 1):1063–1072. - PubMed
-
- Muller NL. Clinical value of high-resolution CT in chronic diffuse lung disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157:1163–1170. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura K, Izumi T, Kitaichi M, Nagai S, Itoh H. The diagnostic accuracy of high-resolution computed tomography in diffuse infiltrative lung diseases. Chest. 1993;104:1149–1155. - PubMed
-
- Scatarige JC, Diette GB, Haponik EF, Merriman B, Fishman EK. Utility of high-resolution CT for management of diffuse lung disease: results of a survey of U.S. pulmonary physicians. Acad Radiol. 2003;10:167–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

