Safety and efficacy of topical interferon alpha 2B and mitomycin C for localized conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia: long-term report of their pharmacological safety and efficacy
- PMID: 37501105
- PMCID: PMC10373405
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-023-03092-z
Safety and efficacy of topical interferon alpha 2B and mitomycin C for localized conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia: long-term report of their pharmacological safety and efficacy
Abstract
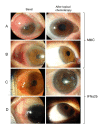
Purpose: Ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) comprises a wide spectrum of squamous tumors, from which corneal/conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is the most common one. The classic treatment is complete excision, but recurrence rates are high. Antineoplastic drugs such as mitomycin C (MMC) and interferon alpha 2b (IFNα2b) have been used as adjuvants or as primary treatment. To evaluate the efficacy and safety of topical IFNα2b and MMC in patients with CIN, a phase IIb double-blind clinical trial was performed.
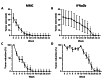
Methods: Patients diagnosed with localized CIN were evaluated by slit lamp and impression cytology and were randomly given MMC 0.04% or INF2b (1 million IU/mL) 4 times daily until neoplasia resolution. Time of resolution and frequency of adverse effects were analyzed to determine the pharmacological efficacy and safety of both medications.
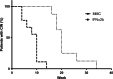
Results: Seventeen patients were included. Nine patients were treated with MMC and 8 with IFNα2b. All patients responded to treatment. The resolution time in days was 59.11 ± 24.02 in patients treated with MMC and 143.50 ± 47.181 in those treated with IFNα2b (p < 0.001). In the MMC group, one recurrence was reported (11%). There were no recurrences at 2 years of follow-up in the IFNα2b group. Regarding adverse effects, one or more mild adverse reaction occurred in 77% of patients managed with MMC and in 50% of patients managed with IFNα2b (p > 0.05). No serious adverse effects were reported.
Conclusions: Topical chemotherapy with MMC and IFNα2b demonstrate pharmacological safety and efficacy. Therefore, these drugs could be considered as primary therapies for localized CIN .
Keywords: Efficacy; Eye drops; Interferon alpha 2b; Mitomycin C; Ocular surface squamous neoplasia; Safety.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of recurrent corneal and conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia with topical interferon alfa 2b.Ophthalmology. 2004 Sep;111(9):1755-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.01.034. Ophthalmology. 2004. PMID: 15350333
-
Topical Interferon α-2b as a Single Therapy for Primary Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia.Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2015 Sep-Oct;4(5):279-82. doi: 10.1097/APO.0000000000000104. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2015. PMID: 26176194
-
Retrospective Comparative Study of Topical Interferon α2b Versus Mitomycin C for Primary Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia.Cornea. 2017 Mar;36(3):327-331. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000001116. Cornea. 2017. PMID: 28079688
-
Topical medical therapies for ocular surface tumors.Semin Ophthalmol. 2006 Jul-Sep;21(3):161-9. doi: 10.1080/08820530500351694. Semin Ophthalmol. 2006. PMID: 16912014 Review.
-
Adjuvant treatment or primary topical monotherapy for ocular surface squamous neoplasia: a systematic review.Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2017 Mar-Apr;80(2):131-136. doi: 10.5935/0004-2749.20170032. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2017. PMID: 28591290
Cited by
-
Pilot clinical trial of neoadjuvant toll-like receptor 7 agonist (Imiquimod) immunotherapy in early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 27;16:1530262. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1530262. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39931064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Case of Conjunctival Melanoma Presenting as a Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 25;15(1):742-750. doi: 10.1159/000541860. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39464315 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

