The role of NPY2R/NFATc1/DYRK1A regulatory axis in sebaceous glands for sebum synthesis
- PMID: 37501148
- PMCID: PMC10375735
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-023-00467-4
The role of NPY2R/NFATc1/DYRK1A regulatory axis in sebaceous glands for sebum synthesis
Abstract
Background: Sebaceous glands (SGs) synthesize and secret sebum to protect and moisturize the dermal system via the complicated endocrine modulation. Dysfunction of SG are usually implicated in a number of dermal and inflammatory diseases. However, the molecular mechanism behind the differentiation, development and proliferation of SGs is far away to fully understand.
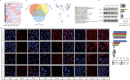
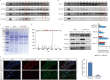
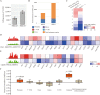
Methods: Herein, the rat volar and mammary tissues with abundant SGs from female SD rats with (post-natal day (PND)-35) and without puberty onset (PND-25) were arrested, and conducted RNA sequencing. The protein complex of Neuropeptide Y receptor Y2 (NPY2R)/NPY5R/Nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 (NFATc1) was performed by immunoprecipitation, mass spectrum and gel filtration. Genome-wide occupancy of NFATc1 was measured by chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing. Target proteins' expression and localization was detected by western blot and immunofluorescence.
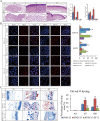
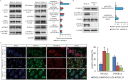
Results: NPY2R gene was significantly up-regulated in volar and mammary SGs of PND-25. A special protein complex of NPY2R/NPY5R/NFATc1 in PND-25. NFATc1 was dephosphorylated and activated, then localized into nucleus to exert as a transcription factor in volar SGs of PND-35. NFATc1 was especially binding at enhancer regions to facilitate the distal SG and sebum related genes' transcription. Dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) contributed to NFATc1 phosphorylation in PND-25, and inactivated of DYRK1A resulted in NFATc1 dephosphorylation and nuclear localization in PND-35.
Conclusions: Our findings unmask the new role of NPY2R/NFATc1/DYRK1A in pubertal SG, and are of benefit to advanced understanding the molecular mechanism of SGs' function after puberty, and provide some theoretical basis for the treatment of acne vulgaris from the perspective of hormone regulation.
Keywords: DYRK1A; NFATc1; NPY2R; NPY5R; Puberty onset; Sebaceous glands.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wang T, Zhou Z, Luo E, Zhong J, Zhao D, Dong H, Yao B. Comprehensive RNA sequencing in primary murine keratinocytes and fibroblasts identifies novel biomarkers and provides potential therapeutic targets for skin-related diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021;26:42. doi: 10.1186/s11658-021-00285-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SKYD2022023/Suzhou Medical health science and technology innovation project
- SKJY2021016/Suzhou Medical health science and technology innovation project
- XYFY202219/Science and Technology Planning Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University
- XYFM202217/Science and Technology Planning Fund of Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University
- GSWS2022111/Gusu Health Talent Research Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

