Cutting-edge advances in modeling the blood-brain barrier and tools for its reversible permeabilization for enhanced drug delivery into the brain
- PMID: 37501215
- PMCID: PMC10373415
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-023-01079-3
Cutting-edge advances in modeling the blood-brain barrier and tools for its reversible permeabilization for enhanced drug delivery into the brain
Abstract
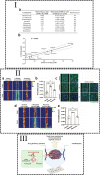
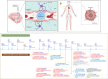
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a sophisticated structure whose full functionality is required for maintaining the executive functions of the central nervous system (CNS). Tight control of transport across the barrier means that most drugs, particularly large size, which includes powerful biologicals, cannot reach their targets in the brain. Notwithstanding the remarkable advances in characterizing the cellular nature of the BBB and consequences of BBB dysfunction in pathology (brain metastasis, neurological diseases), it remains challenging to deliver drugs to the CNS. Herein, we outline the basic architecture and key molecular constituents of the BBB. In addition, we review the current status of approaches that are being explored to temporarily open the BBB in order to allow accumulation of therapeutics in the CNS. Undoubtedly, the major concern in field is whether it is possible to open the BBB in a meaningful way without causing negative consequences. In this context, we have also listed few other important key considerations that can improve our understanding about the dynamics of the BBB.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Drug delivery; Drug targets; Focused ultrasound; In vitro models; In vivo models; Intra-arterial infusion; Organoid models.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.G., P.W., and M.J. are co-owners of Ti-com Polish Limited Liability Company. P.W. and M.J are co-owners of IntraART, LLC. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advances in Targeted Drug Delivery Approaches for the Central Nervous System Tumors: The Inspiration of Nanobiotechnology.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;12(1):84-98. doi: 10.1007/s11481-016-9698-1. Epub 2016 Jul 23. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27449494 Review.
-
The exciting potential of nanotherapy in brain-tumor targeted drug delivery approaches.Neural Regen Res. 2017 Feb;12(2):197-200. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.200796. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 28400793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Targeted Drug Delivery in Central Nervous System Cancers: Advances in Targeting Strategies.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(30):2762-2776. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200826122402. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32851962 Review.
-
Nanoscale drug delivery systems and the blood-brain barrier.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Feb 7;9:795-811. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S52236. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24550672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticles strategies to modify pharmacokinetics of central nervous system targeting drugs: Crossing or circumventing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to manage neurological disorders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Oct;189:114485. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114485. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35970274 Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing neurotherapeutics: blood-brain barrier-on-a-chip technologies for precise drug delivery.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Mar 4;86(5):2794-2804. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001887. eCollection 2024 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38694300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gain efficiency with streamlined and automated data processing: Examples from high-throughput monoclonal antibody production.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 1;20(7):e0326678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326678. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40591905 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid-integrated devices for mimicking malignant brain tumors ("tumor-on-a-chip") for in vitro development of targeted drug delivery and personalized therapy approaches.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 19;11:1452298. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1452298. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39629230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Clec9a in dendritic cell-based tumor immunotherapy for molecular insights and therapeutic potentials.NPJ Vaccines. 2025 Feb 7;10(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41541-025-01084-2. NPJ Vaccines. 2025. PMID: 39920156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing CNS Therapeutics: Enhancing Neurological Disorders with Nanoparticle-Based Gene and Enzyme Replacement Therapies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Feb 4;20:1443-1490. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S457393. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39925682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

