Increased hepatic Akt phosphorylation alleviated glucose intolerance and improved liver function in leptin-deficient mice
- PMID: 37502436
- PMCID: PMC10369657
- DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2023.127849
Increased hepatic Akt phosphorylation alleviated glucose intolerance and improved liver function in leptin-deficient mice
Abstract
Aim of the study: Akt is involved in upregulating the insulin-signaling pathways essential for maintaining glucose metabolism. Glycosphingolipids are involved in the pathogenesis of glucose intolerance and associated target organ injury. On the other hand, oral administration of b-glucosylceramide (GC) has been shown to alleviate insulin resistance. The present study aimed to determine the effects of oral administration of insulin and GC, separately and in combination, on Akt expression and the subsequent effect on metabolic syndrome characteristics in leptin-deficient mice.
Material and methods: Four groups of leptin-deficient ob/ob mice were orally administered for four weeks: vehicle, GC, short-acting insulin, and GC combined with insulin. Mice were followed for hepatic Akt expression and changes in tumor necrosis factor a (TNF-a) level, hyperlipidemia, and liver damage.
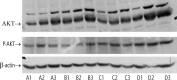
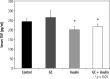
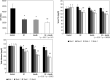
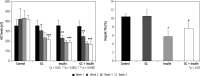
Results: In mice that received insulin or GC, particularly those that received both, the liver phosphorylation of Akt was significantly increased compared to those that received only vehicle. Serum TNF-a levels decreased in insulin-treated mice. These effects were associated with alleviating glucose intolerance and hyperlipidemia, as manifested by a significant glucose tolerance test improvement and reductions in serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels. Significant liver damage alleviation was noted by liver enzyme reductions in all treated groups, along with liver steatosis in the insulin-treated mice.
Conclusions: These data established the potential use of oral insulin administration with glycosphingolipids to alleviate glucose intolerance and associated liver damage and hyperlipidemia via increased Akt expression in the liver. The data support targeting Akt as a potent therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: AKT; NAFLD; TNF-a; diabetes; steatosis.
Copyright © 2023 Clinical and Experimental Hepatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Y. Ilan is a consultant for Teva; ENZO; Protalix; Betalin Therapeutics; Immuron; SciM; Natural Shield; Oberon Sciences; Tiziana Pharma; Plantylight; Exalenz Bioscience. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatic insulin resistance in ob/ob mice involves increases in ceramide, aPKC activity, and selective impairment of Akt-dependent FoxO1 phosphorylation.J Lipid Res. 2015 Jan;56(1):70-80. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M052977. Epub 2014 Nov 13. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25395359 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte TRAF3 promotes insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in mice with obesity.Mol Metab. 2015 Oct 17;4(12):951-60. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.09.013. eCollection 2015 Dec. Mol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26909311 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine restriction prevents the progression of hepatic steatosis in leptin-deficient obese mice.Metabolism. 2013 Nov;62(11):1651-61. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.06.012. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23928105
-
Kombucha tea improves glucose tolerance and reduces hepatic steatosis in obese mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Nov;155:113660. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113660. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36095960
-
Oral administration of immunoglobulin G-enhanced colostrum alleviates insulin resistance and liver injury and is associated with alterations in natural killer T cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2012 Feb;167(2):252-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04511.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22236001 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Constrained Disorder Principle May Account for Consciousness.Brain Sci. 2024 Feb 23;14(3):209. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14030209. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38539598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opaganib Promotes Weight Loss and Suppresses High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 Apr 1;18:969-983. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S514548. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40191829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manna P, Jain SK. Hydrogen sulfide and L-cysteine increase phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) and glucose utilization by inhibiting phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) protein and activating phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/serine/threonine protein kinase (AKT)/protein kinase Czeta/lambda (PKCzeta/lambda) in 3T3l1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 39848-39859. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fuentes M, Santander N, Cortes V. Insulin increases cholesterol uptake, lipid droplet content, and apolipoprotein B secretion in CaCo-2 cells by upregulating SR-BI via a PI3K, AKT, and mTOR-dependent pathway. J Cell Biochem 2019; 120: 1550-1559. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
