The relationship between 6-thioguanine levels and remission outcomes in children with autoimmune hepatitis. Single center experience
- PMID: 37502437
- PMCID: PMC10369651
- DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2023.127442
The relationship between 6-thioguanine levels and remission outcomes in children with autoimmune hepatitis. Single center experience
Abstract
Aim of the study: The treatment of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is based on steroids and azathioprine (AZA). AZA is a pro-drug which is converted among others into 6-thioguanine (6-TG) and 6-methylmercaptopurine (6-MMP). The aim of the study was to determine the relationship between the AZA active metabolite 6-TG and both the biochemical and histological remission outcomes.
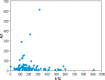
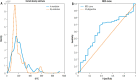
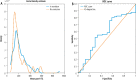
Material and methods: The authors conducted a retrospective analysis of a single chart review. The sample size consisted of 44 pediatric patients with AIH. Biochemical remission was defined as an alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level below 40 U/l and histological remission was defined as a situation when the control biopsy revealed inflammation grade G1 (or lower) in the Batts-Ludwig score. Statistical analysis was applied to assess the difference in remission outcomes in patients with different levels of 6-TG.
Results: In the benchmark variant of our statistical analysis, we found that the correlation between 6-TG and ALT in the sample was not statistically significant. Moreover, the difference between the mean levels of ALT in the populations in and without remission was not statistically significant (the p-value of the t-test was 0.16).
Conclusions: Our results tend to support the claim that there is no statistically significant relationship between 6-TG concentration and remission (both biochemical and histological) in pediatric patients with AIH.
Keywords: 6-thioguanine levels; autoimmune hepatitis; children; remission; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Clinical and Experimental Hepatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jimenez-Riviera C, Ling SC, Ahmed N, et al. Incidence and characteristics of autoimmune hepatitis. Pediatrics 2015; 136: e1237-1248. - PubMed
-
- Deneau M, Jensen MK, Holmen J, et al.. Primary sclerosing cholangitis, autoimmune hepatits, and overlap in Utah children: Epidemiology and natural history. Hepatology 2013; 58: 1392-1400. - PubMed
-
- Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D, Baumann U, et al. Diagnosis and management of pediatric autoimmune liver disease: ESPGHAN Hepatology Committee Position Statement. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2018; 66: 345-360. - PubMed
-
- Bolia R, Rajanayagam J, Hardikar W. Lower 6-MMP/6-TG ratio may be a therapeutic target in pediatric autoimmune hepatitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2018; 67: 695-700. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous