Safety and efficacy of AK0529 in respiratory syncytial virus-infected infant patients: A phase 2 proof-of-concept trial
- PMID: 37502622
- PMCID: PMC10368966
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.13176
Safety and efficacy of AK0529 in respiratory syncytial virus-infected infant patients: A phase 2 proof-of-concept trial
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection is a cause of substantial morbidity and mortality in young children. There is currently no effective therapy available.
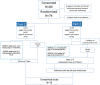
Methods: This was a Phase 2 study of the oral RSV fusion protein inhibitor AK0529 in infants aged 1-24 months, hospitalized with RSV infection. In Part 1, patients (n = 24) were randomized 2:1 to receive a single dose of AK0529 up to 4 mg/kg or placebo. In Part 2, patients (n = 48) were randomized 2:1 to receive AK0529 at 0.5, 1, or 2 mg/kg bid or placebo for 5 days. Sparse pharmacokinetic samples were assessed using population pharmacokinetics modelling. Safety, tolerability, viral load, and respiratory signs and symptoms were assessed daily during treatment.
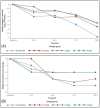
Results: No safety or tolerability signals were detected for AK0529: grade ≥3 treatment-emergent adverse events occurring in 4.1% of patients in AK0529 and 4.2% in placebo groups, respectively, and none led to death or withdrawal from the study. In Part 2, targeted drug exposure was reached with 2 mg/kg bid. A numerically greater reduction in median viral load with 2 mg/kg bid AK0529 than with placebo at 96 h was observed. A -4.0 (95% CI: -4.51, -2.03) median reduction in Wang Respiratory Score from baseline to 96 h was observed in the 2 mg/kg group compared with -2.0 (95% CI: -3.42, -1.82) in the placebo group.
Conclusions: AK0529 was well tolerated in hospitalized RSV-infected infant patients. Treatment with AK0529 2 mg/kg bid was observed to reduce viral load and Wang Respiratory Score.
Clinical trials registration: NCT02654171.
Keywords: AK0529; fusion inhibitor; infants; respiratory syncytial virus (RSV); ziresovir.
© 2023 Shanghai Ark Biopharmaceutical Ltd Co. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
JZW is a co‐inventor of patents (WO2013020993A, 2012; CN105726488B, 2014) covering a compound targeting RSV diseases and a preparation method of the formula. ST and JZW are co‐inventors of a patent (WO2021083290A1; 2020) covering RSV fusion protein inhibitor composition and its use for the treatment and prophylaxis of RSV. FG, ST, GZ, and JZW are or were employees of and are shareholders in Ark Biosciences. JPD served as a compensated scientific consultant for Ark Biosciences and is a shareholder in the company. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shi T, McAllister DA, O'Brien KL, et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: a systematic review and modelling study. Lancet. 2017;390(10098):946‐958. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30938-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cunningham S, Piedra PA, Martinon‐Torres F, et al. Nebulised ALX‐0171 for respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection in hospitalised children: a double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021;9(1):21‐32. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30320-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

