Utility of 3D T2-weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolution (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-flight (TOF) MRA Fusion Imaging in Acute Intracerebral Artery Occlusion
- PMID: 37502657
- PMCID: PMC10370540
- DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2020-0072
Utility of 3D T2-weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolution (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-flight (TOF) MRA Fusion Imaging in Acute Intracerebral Artery Occlusion
Abstract
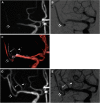
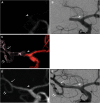
Objective: The course of the vessel affects the success of recanalization and can cause complications in mechanical thrombectomy (MT); however, no study has been reported a method for outlining vessel course prior to MT. We propose magnetic resonance (MR) fusion images as a useful tool in MT for acute ischemic stroke.
Case presentations: A 73-year-old woman and a 79-year-old man were admitted to our hospital with left hemiparesis. In both patients, MR revealed acute ischemic stroke due to right middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion. MR fusion images were created with 3D T2-weighted sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolution (SPACE) and 3D time-of-flight (TOF) MRA acquired before MT clearly revealed the occluded right MCA. In both cases, the fusion image is enabled information about the course of the right MCA and its branches to be obtained prior to performing MT. The thrombi were removed with a stent retriever and reperfusion catheter with no complications, and there was remarkable resolution of symptoms in both patients immediately after the procedure.
Conclusion: A fusion image of T2-weighted SPACE and 3D TOF MRA appears to be a simple and effective method for determining the course of the occluded vessel prior to MT for acute ischemic stroke. This technique will enable good recanalization in MT for acute ischemic stroke and should reduce complications.
Keywords: MRI; acute stroke; thrombectomy.
©2020 The Japanese Society for Neuroendovascular Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Usefulness of the Preoperative Images Supporting Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Susceptibility-Weighted Image for Stroke.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023;17(9):202-208. doi: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2023-0031. Epub 2023 Aug 8. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023. PMID: 37731467 Free PMC article.
-
3D T2-Weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolutions (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-Flight (TOF) MR Angiography Fusion Imaging for Occluded Intracranial Arteries.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022;16(9):452-457. doi: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2021-0102. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 37502793 Free PMC article.
-
A proposed method for outlining occluded intracranial artery using 3D T2-weighted sampling perfection with application optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolution (SPACE).Acta Radiol Open. 2021 Mar 23;10(3):20584601211003233. doi: 10.1177/20584601211003233. eCollection 2021 Mar. Acta Radiol Open. 2021. PMID: 33815831 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of T1- and T2-Weighted High-Resolution Vessel Wall Imaging for the Diagnosis and Follow Up of Isolated Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Dissection with Ischemic Stroke: Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017 Nov;26(11):2645-2651. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.06.038. Epub 2017 Aug 30. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28864037 Review.
-
Successful mechanical thrombectomy in acute bilateral M1 middle cerebral artery occlusion: a case report and literature review.BMC Neurol. 2023 Mar 24;23(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03173-y. BMC Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36964484 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Usefulness of the Preoperative Images Supporting Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Susceptibility-Weighted Image for Stroke.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023;17(9):202-208. doi: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2023-0031. Epub 2023 Aug 8. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023. PMID: 37731467 Free PMC article.
-
3D T2-Weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolutions (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-Flight (TOF) MR Angiography Fusion Imaging for Occluded Intracranial Arteries.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022;16(9):452-457. doi: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2021-0102. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 37502793 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive arteriopathy with vasospasm in focal cerebral arteriopathy in childhood: a case report.BMC Neurol. 2023 Jul 24;23(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03334-z. BMC Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37488477 Free PMC article.
-
The Usefulness of a 3D Roadmap of Occluded Vessels Created from Rapid 3D Proton Density-Weighted Imaging for Mechanical Thrombectomy.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2025;19(1):2024-0044. doi: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2024-0044. Epub 2024 Nov 6. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2025. PMID: 40018276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, et al. : Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016; 387: 1723–1731. - PubMed
-
- Saber H, Narayanan S, Palla M, et al. : Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke with occlusion of the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery: a meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg 2018; 10: 620–624. - PubMed

