What explains the link between romantic conflict with gambling problems? Testing a serial mediational model
- PMID: 37502746
- PMCID: PMC10370473
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1018098
What explains the link between romantic conflict with gambling problems? Testing a serial mediational model
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: What explains the link between romantic conflict with gambling problems? Testing a serial mediational model.Front Psychol. 2023 Nov 3;14:1305966. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1305966. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38022999 Free PMC article.
Abstract
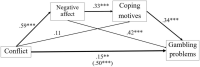
Introduction: While individuals have many motives to gamble, one particularly risky motive for gambling is to cope with negative affect. Conflict with one's romantic partner is a strong predictor of negative affect, which may elicit coping motives for gambling and, in turn, gambling-related problems. Support for this mediational model was demonstrated in relation to drinking-related problems. We extended this model to gambling.
Method: Using a cross-sectional design, we examined links between romantic conflict (Partner-Specific Rejecting Behaviors Scale), negative affect (Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scales-21), coping gambling motives (Gambling Motives Questionnaire, coping subscale), and gambling-related problems [Problem Gambling Severity Index (PGSI)] in 206 regular gamblers (64% men; mean age = 44.7 years; mean PGSI = 8.7) who were in a romantic relationship and recruited through Qualtrics Panels in July 2021.
Results: Results supported our hypothesis that the association between romantic conflict and gambling-related problems would be sequentially mediated through negative affect and coping gambling motives, β = 0.38, 95% CI [0.27, 0.39], and also showed a strong single mediation pathway through negative affect alone, β = 0.27, 95% CI [0.17, 0.38].
Discussion: Negative affect and coping gambling motives partially explain the link between romantic conflict and gambling-related problems. Interventions should target both negative affect and coping gambling motives in response to romantic conflict to reduce gambling-related problems in partnered gamblers.
Keywords: coping motives; gambling; negative affect; problem gambling; romantic conflict.
Copyright © 2023 Hagen, Nogueira-Arjona, Sherry, Rodriguez, Yakovenko and Stewart.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dyadic conflict, drinking to cope, and alcohol-related problems: A psychometric study and longitudinal actor-partner interdependence model.J Fam Psychol. 2015 Oct;29(5):697-707. doi: 10.1037/fam0000098. Epub 2015 Jun 15. J Fam Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26075735
-
Corrigendum: What explains the link between romantic conflict with gambling problems? Testing a serial mediational model.Front Psychol. 2023 Nov 3;14:1305966. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1305966. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38022999 Free PMC article.
-
An Investigation of the Association Between Shame and Problem Gambling: The Mediating Role of Maladaptive Coping Motives.J Gambl Stud. 2017 Dec;33(4):1067-1079. doi: 10.1007/s10899-017-9674-6. J Gambl Stud. 2017. PMID: 28160114
-
Drinking to Cope Mediates the Association between Dyadic Conflict and Drinking Behavior: A Study of Romantic Couples during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jul 10;20(14):6332. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20146332. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37510565 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between financial gambling motives, gambling frequency and level of problem gambling: a meta-analytic review.Addiction. 2022 Mar;117(3):559-569. doi: 10.1111/add.15642. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Addiction. 2022. PMID: 34286879 Review.
Cited by
-
Gambling Disorder and Romantic Relationships: The role of positive communication and emotional dysregulation in couple satisfaction.J Gambl Stud. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1007/s10899-025-10410-1. Online ahead of print. J Gambl Stud. 2025. PMID: 40586831
References
-
- Afifi T. O., Brownridge D. A., MacMillan H., Sareen J. (2010). The relationship of gambling to intimate partner violence and child maltreatment in a nationally representative sample. J. Psychiatric Res. 44 331–337. - PubMed
-
- Aloia L. S., Solomon D. H. (2015). Conflict intensity, family history, and physiological stress reactions to conflict within romantic relationships. Hum. Commun. Res. 41 367–389. 10.1111/hcre.12049 - DOI
-
- American Psychiatric Association [APA] (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing. 10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 - DOI
-
- Antony M. M., Bieling P. J., Cox B. J., Enns M. W., Swinson R. P. (1998). Psychometric properties of the 42-item and 21-item versions of the depression anxiety stress scales in clinical groups and a community sample psychometric properties of the 42-Item and 21-item versions of the depression anxiety stress scales in clinical G. Psychol. Assess. 10 176–181. 10.1037/1040-3590.10.2.176 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources