Clinical Usefulness of Preoperative MCA Anatomical Scanning MRI in Thrombectomy Therapy for Acute Anterior Circulation Vessel Occlusion
- PMID: 37502782
- PMCID: PMC10370890
- DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2020-0118
Clinical Usefulness of Preoperative MCA Anatomical Scanning MRI in Thrombectomy Therapy for Acute Anterior Circulation Vessel Occlusion
Abstract
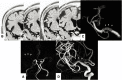
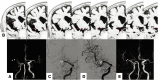
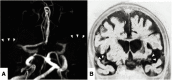
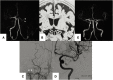
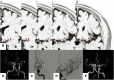
Objective: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the usefulness of the T2-weighted three-dimensional sequence method, known as "basi-parallel anatomical scanning (BPAS)-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)," in demonstrating the running course of the obstructed middle cerebral artery (MCA) before acute mechanical thrombectomy.
Methods: Patients whose M1 part and internal carotid artery (ICA) were occluded on preprocedural MRA, but well demonstrated on MCA anatomical scanning (MAS)-MRI were enrolled in this study. The MAS-MR images for patients in whom thrombectomy was performed were compared with the post-thrombectomy angiography. We compared the running course of the C1-M2 bifurcation on MAS-MRI and angiography after thrombectomy, and the results were classified into 3 groups (Excellent, Good, and Poor).
Results: A total of 13 patients (range: 54-89) were enrolled, among whom 12 underwent thrombectomy. We compared MAS-MRI and post-thrombectomy angiography in 10. On comparison between MAS-MRI and post-procedural angiography, visualization was excellent in six (60%) patients. The mean age was 75.7 years, ranging from 54 to 89, and 6 were males. 3 patients had ICA occlusion and seven had MCA occlusion.
Conclusion: MAS-MRI was considered useful to clarify the running course of the MCA before acute mechanical thrombectomy.
Keywords: MCA anatomical scanning MRI; acute thrombectomy; anterior circulation vessels occlusion.
©2021 The Japanese Society for Neuroendovascular Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, et al. : Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016; 387: 1723–1731. - PubMed
-
- Saver JL, Goyal M, van der Lugt A, et al. : Time to treatment with endovascular thrombectomy and outcomes from ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2016; 316: 1279–1288. - PubMed
-
- Nagahata M, Hosoya T, Adachi M, et al. : Basi-parallel anatomical scanning (BPAS) MRI: a simple MRI technique for demonstrating the surface appearance of the intracranial vertebrobasilar artery. Nihon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi 2003; 63: 582–584. (in Japanese) - PubMed
-
- Shiota H, Oishi M, Kamei S: Diagnosis of vertebrabasilar artery dissection using BPAS (Basi-parallel Anatomical scanning) MRI. J Nihon Univ Med Assoc 2010; 69: 73–74. (in Japanese)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

