3D T2-Weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolutions (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-Flight (TOF) MR Angiography Fusion Imaging for Occluded Intracranial Arteries
- PMID: 37502793
- PMCID: PMC10370984
- DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2021-0102
3D T2-Weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolutions (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-Flight (TOF) MR Angiography Fusion Imaging for Occluded Intracranial Arteries
Abstract
Objective: Determining the course of occluded vessels in advance will increase the success rate and safety of mechanical thrombectomy (MT). Herein, we evaluate the usefulness of MR fusion images created via 3D T2-weighted sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolutions (T2-SPACE) and 3D time-of-flight (TOF)-MRA for visualization of occluded vessels in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) before MT.
Methods: We enrolled 26 patients with AIS caused by intracranial large vessel occlusion who presented at our hospital and underwent MRI with fusion images unaffected by motion artifacts in our study. All patients underwent T2-SPACE and TOF-MRA followed by MT. We created fusion images of the T2-SPACE and TOF-MRA by combining a translucent image of the occluded artery produced by the flow void effect in T2-SPACE with the same vessel in a TOF-MRA image. Fusion images were compared with post-recanalization angiography and post-recanalization MRA, respectively, and the degree of agreement in depiction of M1 runs and M2 branching beyond the occlusion on three levels was assessed. Imaging evaluations were performed independently by two endovascular specialists.
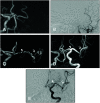
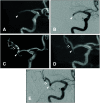
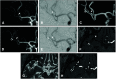
Results: The interobserver agreement of the MRI findings about the concordance of the occluded vessel's run was excellent (kappa was 0.87 [confidence interval: 0.61-1.12]). In all, 21 patients (80.8%) had excellent imaging, four (15.4%) had fair imaging, and one (3.8%) had a divided opinion of the rating between excellent and fair imaging. No cases were judged to be poorly drawn. Even if there was a localized signal loss, its distal portion could be delineated, so it did not affect the estimation of the entire vessel run, and we found that the anatomical structures of the occluded vessels were distinctly visible in the fusion images.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that MR fusion images derived using T2-SPACE and MRA methodologies could determine the courses of occluded vessels prior to MT performed for AIS. Fusion MR imaging may have potential as a preoperative test for ensuring effective and safe MT procedures.
Keywords: T2-weighted sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolutions; acute ischemic stroke; intracranial artery occlusion; magnetic resonance imaging; mechanical thrombectomy.
©2022 The Japanese Society for Neuroendovascular Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Usefulness of the Preoperative Images Supporting Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Susceptibility-Weighted Image for Stroke.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023;17(9):202-208. doi: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2023-0031. Epub 2023 Aug 8. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023. PMID: 37731467 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of 3D T2-weighted Sampling Perfection with Application-optimized Contrasts Using Different Flip Angle Evolution (SPACE) and 3D Time-of-flight (TOF) MRA Fusion Imaging in Acute Intracerebral Artery Occlusion.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2020;14(10):441-446. doi: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2020-0072. Epub 2020 Aug 11. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2020. PMID: 37502657 Free PMC article.
-
A proposed method for outlining occluded intracranial artery using 3D T2-weighted sampling perfection with application optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolution (SPACE).Acta Radiol Open. 2021 Mar 23;10(3):20584601211003233. doi: 10.1177/20584601211003233. eCollection 2021 Mar. Acta Radiol Open. 2021. PMID: 33815831 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of T1- and T2-Weighted High-Resolution Vessel Wall Imaging for the Diagnosis and Follow Up of Isolated Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Dissection with Ischemic Stroke: Report of 4 Cases and Review of the Literature.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017 Nov;26(11):2645-2651. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.06.038. Epub 2017 Aug 30. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28864037 Review.
-
A scoping review of magnetic resonance angiography and perfusion image synthesis.Front Dement. 2024 Nov 11;3:1408782. doi: 10.3389/frdem.2024.1408782. eCollection 2024. Front Dement. 2024. PMID: 39588202 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Usefulness of the Preoperative Images Supporting Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Susceptibility-Weighted Image for Stroke.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023;17(9):202-208. doi: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2023-0031. Epub 2023 Aug 8. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2023. PMID: 37731467 Free PMC article.
-
False positive angiographic aneurysm of the anterior segment of the M1 bifurcation of the middle cerebral artery: a case report.Front Neurol. 2023 Dec 20;14:1327878. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1327878. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38192573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, et al. . Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischemic stroke: A meta- analysis of individual patient data from five randomized trials. Lancet 2016; 387: 1723–1731. - PubMed
-
- Nogueira RG, Jadhav AP, Haussen DC, et al. . Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N Engl J Med 2018; 378: 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Sato K, Hijikata Y, Omura N, et al. . Usefulness of three- dimensional fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition MRI of large vessel occlusion for detecting occluded middle cerebral artery and internal carotid artery before acute mechanical thrombectomy. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 2021; 23: 201–209. - PMC - PubMed

