Prognostic factors for multi-organ dysfunction in pediatric oncology patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit
- PMID: 37503310
- PMCID: PMC10369184
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1192806
Prognostic factors for multi-organ dysfunction in pediatric oncology patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit
Abstract
Background: Pediatric oncology patients who require admission to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) have worse outcomes compared to their non-cancer peers. Although multi-organ dysfunction (MOD) plays a pivotal role in PICU mortality and morbidity, risk factors for MOD have not yet been identified. We aimed to identify risk factors at PICU admission for new or progressive MOD (NPMOD) during the first week of PICU stay.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included all pediatric oncology patients aged 0 to 18 years admitted to the PICU between June 2018 and June 2021. We used the recently published PODIUM criteria for defining multi-organ dysfunction and estimated the association between covariates at PICU baseline and the outcome NPMOD using a multivariable logistic regression model, with PICU admission as unit of study. To study the predictive performance, the model was internally validated by using bootstrap.
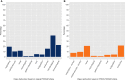
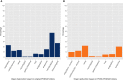
Results: A total of 761 PICU admissions of 571 patients were included. NPMOD was present in 154 PICU admissions (20%). Patients with NPMOD had a high mortality compared to patients without NPMOD, 14% and 1.0% respectively. Hemato-oncological diagnosis, number of failing organs and unplanned admission were independent risk factors for NPMOD. The prognostic model had an overall good discrimination and calibration.
Conclusion: The risk factors at PICU admission for NPMOD may help to identify patients who may benefit from closer monitoring and early interventions. When applying the PODIUM criteria, we found some opportunities for fine-tuning these criteria for pediatric oncology patients, that need to be validated in future studies.
Keywords: critical care; intensive care unit; multi-organ dysfunction; pediatric oncology; prognosis.
Copyright © 2023 Soeteman, Fiocco, Nijman, Bollen, Marcelis, Kilsdonk, Nieuwenhuis, Kappen, Tissing and Wösten-van Asperen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

