Concurrent chemotherapy with partial breast irradiation in triple negative breast cancer patients may improve disease control compared with sequential therapy
- PMID: 37503312
- PMCID: PMC10370352
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1146754
Concurrent chemotherapy with partial breast irradiation in triple negative breast cancer patients may improve disease control compared with sequential therapy
Abstract
Purpose: To report outcomes on a subset of patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) treated on prospective trials with post-lumpectomy partial breast irradiation and concurrent chemotherapy (PBICC) and compare them to a retrospectively assessed similar cohort treated with whole breast irradiation after adjuvant chemotherapy (WBIaC).
Methods and materials: Women with T1-2, N0-1 invasive breast cancer with ≥ 2mm lumpectomy margins were offered therapy on one of two PBICC trials. PBI consisted of 40.5 Gy in 15 daily 2.7 Gy fractions delivered concurrently with the first 2 cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy. The comparison cohort received WBI to a median dose of 60.7 Gy, (including boost, range 42.5 - 66 Gy), after completion of non-concurrent, adjuvant chemotherapy. We evaluated disease-free survival (DFS), and local/loco-regional/distant recurrence-free survival (RFS). We compared survival rates using Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank test of statistical significance.
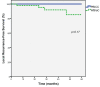
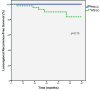
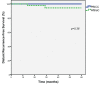
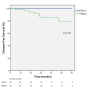
Results: Nineteen patients with TNBC were treated with PBICC on prospective protocol, and 49 received WBIaC. At a median follow-up of 35.5 months (range 4.8-71.9), we observed no deaths in the PBICC cohort and 2 deaths in the WBIaC cohort (one from disease recurrence). With a median time of 23.4 (range 4.8 to 47) months, there were 7 recurrences (1 nodal, 4 local, 4 distant), all in the WBIaC group. At 5 years, there was a trend towards increased local RFS (100% vs. 85.4%, p=0.17) and loco-regional RFS (100% vs. 83.5, p=0.13) favoring the PBICC cohort. There was no significant difference in distant RFS between the two groups (100% vs. 94.4%, p=0.36). Five-year DFS was 100% with PBICC vs.78.9% (95% CI: 63.2 to 94.6%, p=0.08) with WBIaC.
Conclusion: This study suggests that PBICC may offer similar and possibly better outcomes in patients with TNBC compared to a retrospective cohort treated with WBIaC. This observation is hypothesis-generating for prospective trials.
Keywords: breast cancer; clinical trial; concurrent chemoradiation; partial breast irradiation; triple negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Rhome, Wright, De Souza Lawrence, Stearns, Wolff and Zellars.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Choy H, Gerber DE, Bradley JD, Iyengar P, Monberg M, Treat J, et al. Concurrent pemetrexed and radiation therapy in the treatment of patients with inoperable stage III non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review of completed and ongoing studies. Lung Cancer (2015) 87(3):232–40. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.12.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

