Circadian rhythm as a key player in cancer progression as well as a therapeutic target in HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer treatment
- PMID: 37503323
- PMCID: PMC10369080
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1240676
Circadian rhythm as a key player in cancer progression as well as a therapeutic target in HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer treatment
Abstract
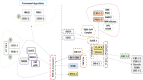
Gastric cancer is one of the most common cancer types with less than one year prognosis in metastatic disease, which poses a huge disease burden. One of the key players in poor prognosis is human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), which also contributes to the pathogenesis of HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer. Trastuzumab is used as first-line chemotherapy that targets the expression of HER2, however, trastuzumab resistance is an inevitable major problem. To overcome this problem, readjustment of the circadian system may play a crucial role, as dysregulation in the expression of circadian clock genes has been observed in tumors. Therefore, pharmacological modulation of clock components can be considered for better efficacy of trastuzumab. In this review, we discuss the association of circadian clock with cancer progression, development, and treatment. Metformin-based chronotherapy can disrupt BMAL1-CLOCK-PER1-HK2 axis, thereby affecting glycolysis oscillation to overcome trastuzumab resistance in HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer.
Keywords: cancer treatment; circadian rhythm; epidermal growth factor receptor 2; gastric cancer; trastuzumab.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Khan, Nabi and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

