Modulation of PD‑L1 expression by standard therapy in head and neck cancer cell lines and exosomes
- PMID: 37503786
- PMCID: PMC10552694
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5550
Modulation of PD‑L1 expression by standard therapy in head and neck cancer cell lines and exosomes
Abstract
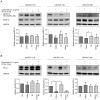
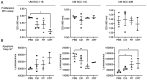
Although checkpoint inhibitors (CPI) have recently extended the treatment options and improved clinical response of advanced stage head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), treatment success remains unpredictable. Programmed cell death ligand‑1 (PD‑L1) is a key player in immunotherapy. Tumor cells, and exosomes derived therefrom, are carriers of PD‑L1 and efficiently suppress immune responses. The aim of the present study was to analyze the influence of established therapies on PD‑L1 expression of HNSCC cell lines and their exosomes. The HNSCC cell lines, UM‑SCC‑11B, UM‑SCC‑14C and UM‑SCC‑22C were treated with fractionated radiotherapy (RT; 5x2 Gy), cisplatin (CT) and cetuximab (Cetux) as monotherapy, or combined therapy, chemoradiotherapy (CRT; RT and CT) or radioimmunotherapy (RT and Cetux). The expression of PD‑L1 and phosphorylated (p)ERK1/2 as a mediator of radioresistance were assessed using western blotting, immunohistochemistry and an ex vivo vital tissue culture model. Additionally, exosomes were isolated from concentrated supernatants of the (un‑)treated HNSCC cell lines by size exclusion chromatography. Exosomal protein expression levels of PD‑L1 were detected using western blotting and semi‑quantitative levels were calculated. The functional impact of exosomes from the (un‑)treated HNSCC cell lines on the proliferation (MTS assay) and apoptosis (Caspase 3/7 assay) of the untreated HNSCC cell lines were measured and compared. The HNSCC cell lines UM‑SCC‑11B and UM‑SCC‑22B showed strong expression of pERK1/2 and PD‑L1, respectively. RT upregulated the PD‑L1 expression in UM‑SCC‑11B and UM‑SCC‑14C and in exosomes from all three cell lines. CT alone induced PD‑L1 expression in all cell lines. CRT induced the expression of PD‑L1 in all HNSCC cell lines and exosomes from UM‑SCC‑14C and UM‑SCC‑22B. The data indicated a potential co‑regulation of PD‑L1 and activated ERK1/2, most evident in UM‑SCC‑14C. Exosomes from irradiated UM‑SCC‑14C cells protected the unirradiated cells from apoptosis by Caspase 3/7 downregulation. The present study suggested a tumor cell‑mediated regulation of PD‑L1 upon platinum‑based CRT in HNSCC and in exosomes. A co‑regulation of PD‑L1 and MAPK signaling response was hypothesized.
Keywords: MAPKs; cetuximab; exosomes; head and neck squamous cell carcinomas; programmed death ligand‑1; small extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
PD‑L1 promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell growth through mTOR signaling.Oncol Rep. 2019 May;41(5):2833-2843. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7053. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30864729 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of EREG via STT3B-mediated N-glycosylation is critical for PDL1 upregulation and immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Oral Sci. 2024 Jul 1;16(1):47. doi: 10.1038/s41368-024-00311-1. Int J Oral Sci. 2024. PMID: 38945975 Free PMC article.
-
The Reversal of Immune Exclusion Mediated by Tadalafil and an Anti-tumor Vaccine Also Induces PDL1 Upregulation in Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Interim Analysis of a Phase I Clinical Trial.Front Immunol. 2019 May 31;10:1206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01206. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31214178 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evolving role of novel radiosensitizers and immune checkpoint inhibitors in (chemo)radiotherapy of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2023 Oct;145:106520. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2023.106520. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Oral Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37467684 Review.
-
Combination of radiation therapy-immunotherapy for head and neck cancers: Promises kept?Cancer Radiother. 2021 Dec;25(8):811-815. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2021.08.018. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Cancer Radiother. 2021. PMID: 34711485 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of chemoradiotherapy on surface PD-L1 expression in esophageal cancer and its implications for immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1509051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1509051. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39763660 Free PMC article.
-
3D Bioprinted Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) Model Using Tunicate Derived Nanocellulose (NC) Bioink.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Mar;14(7):e2403114. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202403114. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 39801216 Free PMC article.
-
The recent progress of tumor cell-derived exosomes in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic strategies of tumors.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 18;23(1):925. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06883-8. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40826466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Up-Regulation of PD-L1 in the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 16;24(22):16386. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216386. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003576 Free PMC article.
-
Influencing immunity: role of extracellular vesicles in tumor immune checkpoint dynamics.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Nov;56(11):2365-2381. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01340-w. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39528800 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G, Jr, Psyrri A, Basté N, Neupane P, Bratland Å, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;394:1915–1928. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gillison ML, Blumenschein G, Jr, Fayette J, Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, Harrington KJ, Kasper S, Vokes EE, Even C, et al. CheckMate 141: 1-Year update and subgroup analysis of nivolumab as first-line therapy in patients with recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer. Oncologist. 2018;23:1079–1082. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0674. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
