Psychological Resilience Interventions for Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37503990
- PMCID: PMC10376838
- DOI: 10.3390/bs13070543
Psychological Resilience Interventions for Adolescents during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
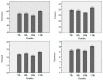
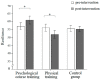
The COVID-19 pandemic has had severe mental health effects on adolescents. Psychological resilience is the ability to recover quickly from adversity and can help adolescents cope with the stress and dangers brought by the pandemic better. Therefore, the current study aimed to explore the developmental pattern of psychological resilience in adolescents and to find the sensitive period for psychological resilience intervention to promote resilience in adolescents during the pandemic. The study measured the psychological resilience of a total of 559 adolescents using the Connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC) in four grades: grade 7 and grade 8 in a junior high school, and grade 10 and grade 11 in a high school. It was found that the resilience level of the adolescents decreased in grade 10 and then increased significantly in grade 11 (F = 4.22, p = 0.006). A 4-week resilience intervention was conducted in the four grades using both psychological course training and physical training. The results revealed that the psychological course training was effective in promoting resilience in the 7th (F = 4.79, p = 0.03) and 8th (F = 4.75, p = 0.03) grades, but not in the 10th and 11th grades. The result suggests that the 7th and 8th grades may be a critical period for psychological resilience interventions for adolescents.
Keywords: COVID-19; adolescents; resilience; resilience intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
All co-authors have expressed agreement with the order of authorship and contents of the manuscript. The authors have no conflict of interests that might be interpreted as influencing the research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Psychological first aid intervention: rescue from psychological distress and improving the pre-licensure nursing students' resilience amidst COVID-19 crisis and beyond.Sci Afr. 2023 Mar;19:e01472. doi: 10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01472. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Sci Afr. 2023. PMID: 36506753 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological Resilience Among Older Japanese Adults With Mild Cognitive Impairment During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jun 10;13:898990. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.898990. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35757230 Free PMC article.
-
Moderating Role of Resilience Between Depression and Stress Response of Vocational Middle School Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 1;13:904592. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.904592. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35845471 Free PMC article.
-
Supporting adolescents' mental health during COVID-19 by utilising lessons from the aftermath of the Great East Japan Earthquake.Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2022;9(1):332. doi: 10.1057/s41599-022-01330-1. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2022. PMID: 36187842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescent Resilience during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of the Impact of the Pandemic on Developmental Milestones.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Jul 1;12(7):220. doi: 10.3390/bs12070220. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35877290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resilience among Turkish adolescents: A multi-level approach.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 1;19(7):e0300165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300165. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38950024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2023. [(accessed on 1 December 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/data/
-
- Dixit S., Musa A., Sillva A.B., Reddy R.S., Abohashrh M., Kakaraparthi V.N., Asiri F., Caruso F.R., Govindappa S.K., Mohammed A.A. The impact of post-traumatic stress of SARS-CoV-2 affliction on psychological and mental health of student survivors: Cross sectional study. Front. Public Health. 2022;10:845741. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.845741. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

