Progress in Isolation and Molecular Profiling of Small Extracellular Vesicles via Bead-Assisted Platforms
- PMID: 37504087
- PMCID: PMC10377709
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13070688
Progress in Isolation and Molecular Profiling of Small Extracellular Vesicles via Bead-Assisted Platforms
Abstract
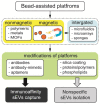
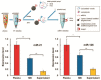
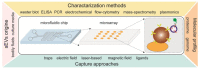
Tremendous interest in research of small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) is driven by the participation of vesicles in a number of biological processes in the human body. Being released by almost all cells of the body, sEVs present in complex bodily fluids form the so-called intercellular communication network. The isolation and profiling of individual fractions of sEVs secreted by pathological cells are significant in revealing their physiological functions and clinical importance. Traditional methods for isolation and purification of sEVs from bodily fluids are facing a number of challenges, such as low yield, presence of contaminants, long-term operation and high costs, which restrict their routine practical applications. Methods providing a high yield of sEVs with a low content of impurities are actively developing. Bead-assisted platforms are very effective for trapping sEVs with high recovery yield and sufficient purity for further molecular profiling. Here, we review recent advances in the enrichment of sEVs via bead-assisted platforms emphasizing the type of binding sEVs to the bead surface, sort of capture and target ligands and isolation performance. Further, we discuss integration-based technologies for the capture and detection of sEVs as well as future research directions in this field.
Keywords: beads; exosomes; isolation; liquid biopsy; molecular characterization; small extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brennan K., Martin K., FitzGerald S.P., O’Sullivan J., Wu Y., Blanco A., Richardson C., Mc Gee M.M. A Comparison of Methods for the Isolation and Separation of Extracellular Vesicles from Protein and Lipid Particles in Human Serum. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:1039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57497-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

