Exploring Key Biomarkers and Common Pathogenesis of Seven Digestive System Cancers and Their Correlation with COVID-19
- PMID: 37504265
- PMCID: PMC10378662
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45070349
Exploring Key Biomarkers and Common Pathogenesis of Seven Digestive System Cancers and Their Correlation with COVID-19
Abstract
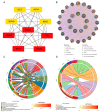
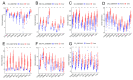
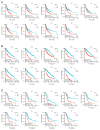
Digestive system cancer and COVID-19 significantly affect the digestive system, but the mechanism of interaction between COVID-19 and the digestive system cancers has not been fully elucidated. We downloaded the gene expression of COVID-19 and seven digestive system cancers (oral, esophageal, gastric, colorectal, hepatocellular, bile duct, pancreatic) from GEO and identified hub differentially expressed genes. Multiple verifications, diagnostic efficacy, prognostic analysis, functional enrichment and related transcription factors of hub genes were explored. We identified 23 common DEGs for subsequent analysis. CytoHubba identified nine hub genes (CCNA2, CCNB1, CDKN3, ECT2, KIF14, KIF20A, KIF4A, NEK2, TTK). TCGA and GEO data validated the expression and excellent diagnostic and prognostic ability of hub genes. Functional analysis revealed that the processes of cell division and the cell cycle were essential in COVID-19 and digestive system cancers. Furthermore, six related transcription factors (E2F1, E2F3, E2F4, MYC, TP53, YBX1) were involved in hub gene regulation. Via in vitro experiments, CCNA2, CCNB1, and MYC expression was verified in 25 colorectal cancer tissue pairs. Our study revealed the key biomarks and common pathogenesis of digestive system cancers and COVID-19. These may provide new ideas for further mechanistic research.
Keywords: COVID-19; common biomarkers; diagnosis; digestive system cancers; pathogenesis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Screening Hub Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2019 Dec;28(1_suppl):76S-86S. doi: 10.1177/0963689719893950. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31822116 Free PMC article.
-
[Bioinformatics analysis of core differentially expressed genes in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2022 Nov 21;34(5):507-513. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2021292. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36464255 Chinese.
-
Identification of Multiple Hub Genes and Pathways in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jul 12;2021:8849415. doi: 10.1155/2021/8849415. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34337056 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals Influence Hub Genes Associated with Aggressive Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 6;24(4):3191. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043191. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834602 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis based on Multiple Databases Identifies Hub Genes Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Genomics. 2019 Aug;20(5):349-361. doi: 10.2174/1389202920666191011092410. Curr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 32476992 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring common pathogenic association between Epstein Barr virus infection and long-COVID by integrating RNA-Seq and molecular dynamics simulations.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1435170. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1435170. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39391317 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and mechanism analysis of biomarkers related to butyrate metabolism in COVID-19 patients.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2477301. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2477301. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40074706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdeljaoued S., Arfa S., Kroemer M., Ben Khelil M., Vienot A., Heyd B., Loyon R., Doussot A., Borg C. Tissue-resident memory T cells in gastrointestinal cancer immunology and immunotherapy: Ready for prime time? J. Immunother. Cancer. 2022;10:e003472. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003472. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

