How Plants Tolerate Salt Stress
- PMID: 37504290
- PMCID: PMC10378706
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45070374
How Plants Tolerate Salt Stress
Abstract
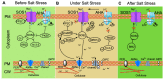
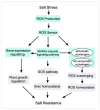
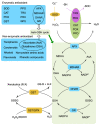
Soil salinization inhibits plant growth and seriously restricts food security and agricultural development. Excessive salt can cause ionic stress, osmotic stress, and ultimately oxidative stress in plants. Plants exclude excess salt from their cells to help maintain ionic homeostasis and stimulate phytohormone signaling pathways, thereby balancing growth and stress tolerance to enhance their survival. Continuous innovations in scientific research techniques have allowed great strides in understanding how plants actively resist salt stress. Here, we briefly summarize recent achievements in elucidating ionic homeostasis, osmotic stress regulation, oxidative stress regulation, and plant hormonal responses under salt stress. Such achievements lay the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of plant salt-tolerance mechanisms.
Keywords: SOS pathway; ionic stress; osmotic stress; oxidative stress; phytohormone; salt stress.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus sp. BSE01 alleviates salt toxicity in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by conserving ionic, osmotic, redox and hormonal homeostasis.Physiol Plant. 2023 Nov-Dec;175(6):e14076. doi: 10.1111/ppl.14076. Physiol Plant. 2023. PMID: 38148224
-
Mechanisms of Plant Responses and Adaptation to Soil Salinity.Innovation (Camb). 2020 Apr 24;1(1):100017. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100017. eCollection 2020 May 21. Innovation (Camb). 2020. PMID: 34557705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome profiling at osmotic and ionic phases of salt stress response in bread wheat uncovers trait-specific candidate genes.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Sep 16;20(1):428. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02616-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32938380 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling salt stress signaling in plants.J Integr Plant Biol. 2018 Sep;60(9):796-804. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12689. Epub 2018 Jul 15. J Integr Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29905393 Review.
-
Regulation of Plant Responses to Salt Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 28;22(9):4609. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094609. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the mechanism of E3 ubiquitin ligases in plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses and perspectives on PROTACs for crop resistance.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Oct;22(10):2811-2843. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14407. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38864414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding of Plant Salt Tolerance Mechanisms and Application to Molecular Breeding.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10940. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010940. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Salicylic Acid in Salinity Stress Mitigation in Dizygostemon riparius: A Medicinal Species Native to South America.Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 4;13(21):3111. doi: 10.3390/plants13213111. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39520029 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium foliar application alleviates salinity stress in sweet william (Dianthus barbatus L.) by enhancing growth and reducing oxidative damage.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 15;15(1):5570. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89463-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39955337 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas-mediated adaptation of Thermus thermophilus HB8 to environmental stress conditions.Arch Microbiol. 2025 Jan 23;207(2):41. doi: 10.1007/s00203-025-04246-x. Arch Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39847105
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

