The Role of Genetic Risk Factors in Pathogenesis of Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 37504294
- PMCID: PMC10378459
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45070378
The Role of Genetic Risk Factors in Pathogenesis of Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
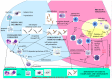
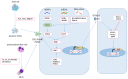
The pathogenesis of childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (cSLE) is complex and not fully understood. It involves three key factors: genetic risk factors, epigenetic mechanisms, and environmental triggers. Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of the disease, particularly in younger individuals. While cSLE has traditionally been considered a polygenic disease, it is now recognized that in rare cases, a single gene mutation can lead to the disease. Although these cases are uncommon, they provide valuable insights into the disease mechanism, enhance our understanding of pathogenesis and immune tolerance, and facilitate the development of targeted treatment strategies. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of both monogenic and polygenic SLE, emphasizing the implications of specific genes in disease pathogenesis. By conducting a thorough analysis of the genetic factors involved in SLE, we can improve our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of the disease. Furthermore, this knowledge may contribute to the identification of effective biomarkers and the selection of appropriate therapies for individuals with SLE.
Keywords: childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus; genetics; monogenic systemic lupus erythematosus; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Klein-Gitelman M.S., Beresford M.W. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Mixed Connective Tissue Disease, and Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease. In: Mellins E.D., Petty R.E., Laxer R.M., Lindsley C.B., Wedderburn L., Fuhlbrigge R.C., editors. Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology. 8th ed. Elsevier; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2021. pp. 295–329.
-
- Edworthy S.M. Clinical manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Harris E.D., Budd R.C., Firestein G.S., editors. Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. 7th ed. WB Saunders; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2005. pp. 1201–1224.
-
- Hoffman I.E., Lauwerys B.R., De Keyser F., Huizinga T.W., Isenberg D., Cebecauer L., Dehoorne J., Joos R., Hendrickx G., Houssiau F., et al. Juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: Different clinical and serological pattern than adult-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009;68:412–415. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.094813. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

