Polymer-Based Hydrogels Applied in Drug Delivery: An Overview
- PMID: 37504402
- PMCID: PMC10379988
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9070523
Polymer-Based Hydrogels Applied in Drug Delivery: An Overview
Abstract
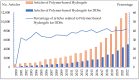
Polymer-based hydrogels are hydrophilic polymer networks with crosslinks widely applied for drug delivery applications because of their ability to hold large amounts of water and biological fluids and control drug release based on their unique physicochemical properties and biocompatibility. Current trends in the development of hydrogel drug delivery systems involve the release of drugs in response to specific triggers such as pH, temperature, or enzymes for targeted drug delivery and to reduce the potential for systemic toxicity. In addition, developing injectable hydrogel formulations that are easily used and sustain drug release during this extended time is a growing interest. Another emerging trend in hydrogel drug delivery is the synthesis of nano hydrogels and other functional substances for improving targeted drug loading and release efficacy. Following these development trends, advanced hydrogels possessing mechanically improved properties, controlled release rates, and biocompatibility is developing as a focus of the field. More complex drug delivery systems such as multi-drug delivery and combination therapies will be developed based on these advancements. In addition, polymer-based hydrogels are gaining increasing attention in personalized medicine because of their ability to be tailored to a specific patient, for example, drug release rates, drug combinations, target-specific drug delivery, improvement of disease treatment effectiveness, and healthcare cost reduction. Overall, hydrogel application is advancing rapidly, towards more efficient and effective drug delivery systems in the future.
Keywords: biopolymers; drug delivery; hydrogels; multi-sensitive hydrogels; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hubbell J.A. Hydrogel systems for barriers and local drug delivery in the control of wound healing. J. Control. Release. 1996;39:305–313. doi: 10.1016/0168-3659(95)00162-X. - DOI
-
- Hubbell J.A. Synthetic biodegradable polymers for tissue engineering and drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 1998;3:246–251. doi: 10.1016/S1359-0286(98)80098-3. - DOI
-
- Perrie Y., Rades T. Pharmaceutics—Drug Delivery and Targeting. 2nd ed. Pharmaceutical Press; London, UK: 2009. pp. 1–240.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

