Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review
- PMID: 37504410
- PMCID: PMC10378855
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9070530
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Hydrogel for Wound Healing; Systematic Review
Abstract
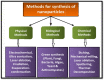
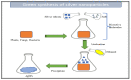
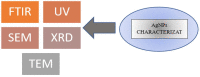
Wound healing is a biological process that involves a series of consecutive process, and its impairment can lead to chronic wounds and various complications. Recently, there has been a growing interest in employing nanotechnology to enhance wound healing. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have expanded significant attention due to their wide range of applications in the medical field. The advantages of AgNPs include their easy synthesis, change their shape, and high surface area. Silver nanoparticles are very efficient for topical drug administration and wound healing because of their high ratio of surface area to volume. The efficiency of AgNPs depends on the synthesis method and the intended application. Green synthesis methods offer an eco-friendly approach by utilizing natural sources such as plant extracts and fungus. The characterization of nanoparticles plays an important character, and it is accomplished through the use of several characterization methods such as UV-Vis spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). These techniques are employed to confirm the specific characters of the prepared Silver Nanoparticles. Additionally, the review addresses the challenges and future perspectives of utilizing green-synthesized AgNPs loaded in Polyacrylamide hydrogel for wound healing applications, including the optimization of nanoparticle size, and release kinetics. Overall, this review highlights the potential of green-synthesized AgNPs loaded in Polyacrylamide hydrogel as promising for advanced wound healing therapies. There are different approaches of usage of AgNPs for wound healing such as polyacrylamide -hydrogels, and the mechanism after their antibacterial action, have been exposed.
Keywords: characterization methods; green synthesis; polyacrylamide hydrogel; silver nanoparticles; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Green Synthesis and Evaluation of Lepidium didymum-mediated Silver Nanoparticles for in vitro Antibacterial Activity and Wound Healing in the Animal Model.J Oleo Sci. 2023 Mar 30;72(4):429-439. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess22380. Epub 2023 Mar 10. J Oleo Sci. 2023. PMID: 36908177
-
Bioactive compound loaded stable silver nanoparticle synthesis from microwave irradiated aqueous extracellular leaf extracts of Naringi crenulata and its wound healing activity in experimental rat model.Acta Trop. 2014 Jul;135:55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Acta Trop. 2014. PMID: 24681224
-
Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Melia azedarach: Enhancement of Antibacterial, Wound Healing, Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Activities.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Dec 11;14:9823-9836. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S231340. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31849471 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Silver Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Versatile Bio-Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 21;16(9):1232. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16091232. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39339268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Green Synthesis of Silver-Based Nanoparticles: Antimicrobial and Antifungal Properties in Various Films.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Feb 7;15(4):252. doi: 10.3390/nano15040252. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39997815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silver nanoparticles loaded with pomegranate peel extract and hyaluronic acid mediate recovery of cutaneous wounds infected with Candida albicans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Nov 29;14:1469493. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1469493. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39679196 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Metal and Metal Oxide Nanomaterials for Topical Antimicrobial Applications: Insights and Future Perspectives.Molecules. 2024 Nov 25;29(23):5551. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235551. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Application of Silver Nanoparticles for Enhancing Phototherapy Outcomes.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;18(7):970. doi: 10.3390/ph18070970. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of inorganic nanoparticles for revolutionary drug delivery applications: a critical review.Discov Nano. 2023 Dec 19;18(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s11671-023-03943-0. Discov Nano. 2023. PMID: 38112849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green catalyst of cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles using petai peel extract for the synthesis of thiazolidinedione-based chalcone 4H-thiopyran as an antioxidant.RSC Adv. 2024 Aug 5;14(34):24384-24397. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03077j. eCollection 2024 Aug 5. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39108969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Augustine R., Kalarikkal A., Thomas S. PCL membranes incorporated with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as antibacterial wound dressings. Appl. Nanosci. 2016;6:337–344. doi: 10.1007/s13204-015-0439-1. - DOI
-
- García-Villén F., Faccendini A., Aguzzi C., Cerezo P., Bonferoni M.C., Rossi S., Grisoli P., Ruggeri M., Ferrari F., Sandri G., et al. Montmorillonite-Norfloxacin nanocomposite intended for healing of infected wounds. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019;14:5051–5060. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S208713. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Satarupa B., Kumari V., Shatabdi D., Moumita., Dutta D.M., Jyotsna M., Sandhimita M., Arnab G. Antibacterial, anti-biofilm activity and mechanism of action of pancreatin doped zinc oxide nanoparticles against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Colloid Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2020;11:190. - PubMed
-
- Kardan-Yamchi J., Kazemian H., Battaglia S., Abtahi H., Foroushani A.R., Hamzelou G., Cirillo D.M., Ghodousi A., Feizabadi M.M. Whole genome sequencing results associated with minimum inhibitory concentrations of 14 anti-tuberculosis drugs among rifampicin-resistant isolates of mycobacterium tuberculosis from Iran. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:465. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020465. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

