Short-Term Prognostic Value of the Culprit-SYNTAX Score in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 37504526
- PMCID: PMC10380831
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10070270
Short-Term Prognostic Value of the Culprit-SYNTAX Score in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: The SYNergy between Percutaneous Coronary Intervention with TAXus and Cardiac Surgery (SYNTAX) score is a scoring system that helps to decide on surgery or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI), and studies are showing the prognostic value of this scoring system in both AMI and coronary artery disease patients undergoing PCI. In acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients, the infarct-related artery and the complexity of the lesions are also important in terms of mortality and morbidity. Our study aimed to determine the prognostic value of the culprit vessel's SYNTAX score (cul-SS) in patients presenting with MI.
Methods: In our study, 1284 patients presenting with MI were analyzed retrospectively. The SYNTAX scores and cul-SS of the patients were calculated. In-hospital and 30-day deaths and major complications were accepted as primary outcomes. The SYNTAX scores and cul-SS were compared in terms of predicting primary outcomes.
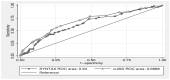
Conclusions: Major complications were observed in 36 (2.8%) patients, death in 42 (3.3%) patients, and stent thrombosis in 24 (1.9%) patients. The area under the curves for SYNTAX and cul-SS for predicting primary outcomes is 0.64 and 0.68 (p = 0.026), respectively. Cul-SS was as successful as the SYNTAX score in predicting stent thrombosis and was superior in predicting short-term death and major complications.
Keywords: ST-elevation myocardial infarction; SYNTAX score; culprit-SYNTAX score; non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction; percutaneous coronary intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Thuijs D.J.F.M., Kappetein A.P., Serruys P.W., Mohr F.W., Morice M.C., Mack M.J., Holmes D.R., Jr., Curzen N., Davierwala P., Noack T., et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with three-vessel or left main coronary artery disease: 10-year follow-up of the multicentre randomised controlled SYNTAX trial. Lancet. 2019;394:1325–1334. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31997-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Head S.J., Milojevic M., Daemen J., Ahn J.M., Boersma E., Christiansen E.H., Domanski M.J., Farkouh M.E., Flather M., Fuster V., et al. Mortality after coronary artery bypass grafting versus percutaneous coronary intervention with stenting for coronary artery disease: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet. 2018;391:939–948. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30423-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yadav M., Palmerini T., Caixeta A., Madhavan M.V., Sanidas E., Kirtane A.J., Stone G.W., Généreux P. Prediction of coronary risk by SYNTAX and derived scores: Synergy between percutaneous coronary intervention with taxus and cardiac surgery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013;62:1219–1230. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.06.047. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Farooq V., Serruys P.W., Bourantas C., Vranckx P., Diletti R., Garcia H.M., Holmes D.R., Kappetein A.P., Mack M., Feldman T., et al. Incidence and multivariable correlates of long-term mortality in patients treated with surgical or percutaneous revascularization in the synergy between percutaneous coronary intervention with taxus and cardiac surgery (SYNTAX) trial. Eur. Heart J. 2012;33:3105–3113. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs367. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous