Combined System for the Simultaneous Delivery of Levofloxacin and Rifampicin: Structural and Functional Properties and Antibacterial Activity
- PMID: 37504876
- PMCID: PMC10381656
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14070381
Combined System for the Simultaneous Delivery of Levofloxacin and Rifampicin: Structural and Functional Properties and Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
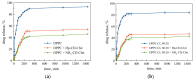
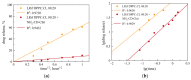
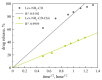
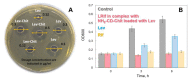
The therapy of resistant forms of tuberculosis requires the simultaneous use of several drugs, in particular, a combination of rifampicin and levofloxacin. In this paper, we aimed to design a combined system for the simultaneous delivery of these drugs for potential inhalation administration. A feature of this system is the incorporation of rifampicin into optimized liposomal vesicles capable of forming a multipoint non-covalent complex with chitosan-β-cyclodextrin conjugates. Levofloxacin is incorporated into cyclodextrin tori by forming a host-guest complex. Here, a comprehensive study of the physicochemical properties of the obtained systems was carried out and special attention was paid to the kinetics of cargo release for individual drugs and in the combined system. The release of levofloxacin in combined system is slow and is described by the Higuchi model in all cases. The release of rifampicin from liposomes during the formation of complexes with polymeric conjugates is characterized by the change of the Higuchi model to the Korsmeyer-Peppas model with the main type of diffusion against Fick's law. Microbiological studies in solid and liquid growth media a consistently high antibacterial activity of the obtained systems was shown against B. subtilis and E. coli.
Keywords: antibiotics; chitosan; cyclodextrin; levofloxacin; liposomes; rifampicin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

