Convenient and Controllable Synthesis of Poly(2-oxazoline)-Conjugated Doxorubicin for Regulating Anti-Tumor Selectivity
- PMID: 37504877
- PMCID: PMC10381835
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14070382
Convenient and Controllable Synthesis of Poly(2-oxazoline)-Conjugated Doxorubicin for Regulating Anti-Tumor Selectivity
Abstract
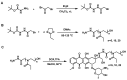
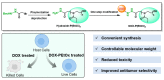
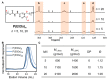
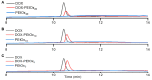
Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-doxorubicin (DOX) conjugation is an important strategy to improve toxicity and enhance clinically therapeutic efficacy. However, with the frequent use of PEG-modified drugs, the accumulation of anti-PEG antibodies has become a tough issue, which limits the application of PEG-drug conjugation. As an alternative solution, poly(2-oxazoline) (POX)-DOX conjugation has shown great potential in the anti-tumor field, but the reported conjugation process of POX with DOX has drawbacks such as complex synthetic steps and purification. Herein, we propose a convenient and controllable strategy for the synthesis of POX-DOX conjugation with different chain lengths and narrow dispersity by N-boc-2-bromoacetohydrazide-initiated 2-ethyl-oxazoline polymerization and the subsequent deprotection of the N-Boc group and direct reaction with DOX. The DOX-PEtOx conjugates were firstly purified, and the successful conjugations were confirmed through various characterization methods. The synthetic DOX-PEtOxn conjugates reduce the toxicity of DOX and increase the selectivity to tumor cells, reflecting the promising application of this POX-DOX conjugation strategy in drug modification and development.
Keywords: anti-tumor selectivity; facile synthesis; poly(2-oxazoline); poly(2-oxazoline)-doxorubicin conjugation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

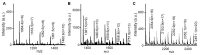
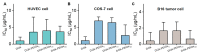
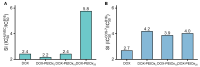
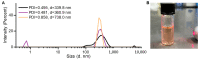
References
-
- Li F., He J., Zhang M., Ni P. A pH-sensitive and Biodegradable Supramolecular Hydrogel Constructed from a PEGylated Polyphosphoester-doxorubicin Prodrug and α-cyclodextrin. Polym. Chem. 2015;6:5009–5014. doi: 10.1039/C5PY00620A. - DOI
-
- Zayed G.M., Kamal I., Abdelhafez W.A., Fahd M.A., Amin M.A., Shaykoon M.S.A., Sarhan H.A., Abdelsalam A.M. Effect of Chemical Binding of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride to Gold Nanoparticles, Versus Electrostatic Adsorption, on the In Vitro Drug Release and Cytotoxicity to Breast Cancer Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018;35:112. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2393-6. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2022M710050/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
- BX2021102/China National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents
- 20XD1421400/Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader
- 2021Szvup042/Free exploring basic research project at Shenzhen Research Institute of ECUST
- Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences/Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Polymer Physics and Chemistry
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

