Ircinia ramosa Sponge Extract (iSP) Induces Apoptosis in Human Melanoma Cells and Inhibits Melanoma Cell Migration and Invasiveness
- PMID: 37504902
- PMCID: PMC10381260
- DOI: 10.3390/md21070371
Ircinia ramosa Sponge Extract (iSP) Induces Apoptosis in Human Melanoma Cells and Inhibits Melanoma Cell Migration and Invasiveness
Abstract
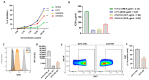
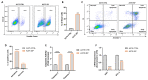
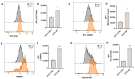
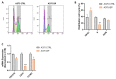
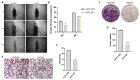
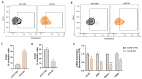
Marine compounds represent a varied source of new drugs with potential anticancer effects. Among these, sponges, including those belonging to the Irciniidae family, have been demonstrated to exert cytotoxic effects on different human cancer cells. Here, we investigated, for the first time, the therapeutic effect of an extract (referred as iSP) from the sponge, Ircinia ramosa (Porifera, Dictyoceratida, and Irciniidae), on A375 human melanoma cells. We found that iSP impaired A375 melanoma cells proliferation, induced cell death through caspase-dependent apoptosis and arrested cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, as demonstrated via both flow cytometry and qPCR analysis. The proapoptotic effect of iSP is associated with increased ROS production and mitochondrial modulation, as observed by using DCF-DHA and mitochondrial probes. In addition, we performed wound healing, invasion and clonogenic assays and found that iSP was able to restrain A375 migration, invasion and clonogenicity. Importantly, we observed that an iSP treatment modulated the expression of the EMT-associated epithelial markers, E-CAD and N-CAD, unveiling the mechanism underlying the effect of iSP in modulating A375 migration and invasion. Collectively, this study provides the first evidence to support the role of Ircinia ramosa sponge extracts as a potential therapeutic resource for the treatment of human melanoma.
Keywords: EMT; Ircinia ramosa; ROS; apoptosis; marine compounds; melanoma; sponges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

