Brevetoxin versus Brevenal Modulation of Human Nav1 Channels
- PMID: 37504927
- PMCID: PMC10382042
- DOI: 10.3390/md21070396
Brevetoxin versus Brevenal Modulation of Human Nav1 Channels
Abstract
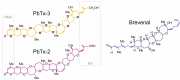
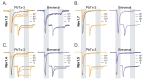
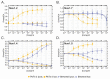
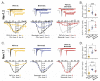
Brevetoxins (PbTx) and brevenal are marine ladder-frame polyethers. PbTx binds to and activates voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channels in native tissues, whereas brevenal antagonizes these actions. However, the effects of PbTx and brevenal on recombinant Nav channel function have not been systematically analyzed. In this study, the PbTx-3 and brevenal modulation of tissue-representative Nav channel subtypes Nav1.2, Nav1.4, Nav1.5, and Nav1.7 were examined using automated patch-clamp. While PbTx-3 and brevenal elicit concentration-dependent and subtype-specific modulatory effects, PbTx-3 is >1000-fold more potent than brevenal. Consistent with effects observed in native tissues, Nav1.2 and Nav1.4 channels were PbTx-3- and brevenal-sensitive, whereas Nav1.5 and Nav1.7 appeared resistant. Interestingly, the incorporation of brevenal in the intracellular solution caused Nav channels to become less sensitive to PbTx-3 actions. Furthermore, we generated a computational model of PbTx-2 bound to the lipid-exposed side of the interface between domains I and IV of Nav1.2. Our results are consistent with competitive antagonism between brevetoxins and brevenal, setting a basis for future mutational analyses of Nav channels' interaction with brevetoxins and brevenal. Our findings provide valuable insights into the functional modulation of Nav channels by brevetoxins and brevenal, which may have implications for the development of new Nav channel modulators with potential therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Nav; PbTx-2; PbTx-3; brevenal; brevetoxins; ladder-frame polyethers; voltage-gated sodium channels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
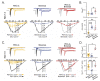
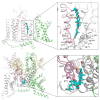
Similar articles
-
The effect of brevenal on brevetoxin-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes.Arch Toxicol. 2005 Nov;79(11):683-8. doi: 10.1007/s00204-005-0676-2. Epub 2005 Jun 29. Arch Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15986201 Free PMC article.
-
Brevenal, a brevetoxin antagonist from Karenia brevis, binds to a previously unreported site on mammalian sodium channels.Harmful Algae. 2013 Jun;26:12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2013.03.001. Harmful Algae. 2013. PMID: 23789024 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologically Targeting the Fibroblast Growth Factor 14 Interaction Site on the Voltage-Gated Na+ Channel 1.6 Enables Isoform-Selective Modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13541. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413541. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948337 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based assessment of disease-related mutations in human voltage-gated sodium channels.Protein Cell. 2017 Jun;8(6):401-438. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0372-z. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Protein Cell. 2017. PMID: 28150151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels.J Mol Biol. 2021 Aug 20;433(17):166967. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166967. Epub 2021 Mar 29. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33794261 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated Patch Clamp for the Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Pufferfish Samples.Mar Drugs. 2024 Apr 15;22(4):176. doi: 10.3390/md22040176. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38667793 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Effects of Brevetoxin-3 Administered via Oral Gavage to Mice.Mar Drugs. 2023 Dec 16;21(12):644. doi: 10.3390/md21120644. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 38132965 Free PMC article.
-
Karenia brevis Extract Induces Cellular Entry through Distinct Mechanisms in Phagocytic RAW 264.7 Macrophages versus Non-Phagocytic Vero Cells.Mar Drugs. 2023 Dec 19;22(1):4. doi: 10.3390/md22010004. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 38276642 Free PMC article.
-
A High-Throughput Biosensing Approach for Rapid Screening of Compounds Targeting the hNav1.1 Channel: Marine Toxins as a Case Study.Mar Drugs. 2025 Mar 9;23(3):119. doi: 10.3390/md23030119. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40137305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACS Molecule of the Week: Brevetoxins. [(accessed on 15 January 2023)]. Available online: https://www.acs.org/molecule-of-the-week/archive/b/brevetoxins.html.
-
- Pierce R.H., Henry M.S., Blum P.C., Osborn S.E., Cheng Y.S., Zhou Y., Irvin C.M., Bourdelais A.J., Naar J., Baden D.G. Compositional changes in neurotoxins and their oxidative derivatives from the dinoflagellate, Karenia brevis, in seawater and marine aerosol. J. Plankton Res. 2011;33:343–348. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbq115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

