Serum identification of at-risk MASH: The metabolomics-advanced steatohepatitis fibrosis score (MASEF)
- PMID: 37505221
- PMCID: PMC10718221
- DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000542
Serum identification of at-risk MASH: The metabolomics-advanced steatohepatitis fibrosis score (MASEF)
Abstract
Background: Early identification of those with NAFLD activity score ≥ 4 and significant fibrosis (≥F2) or at-risk metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is a priority as these patients are at increased risk for disease progression and may benefit from therapies. We developed and validated a highly specific metabolomics-driven score to identify at-risk MASH.
Methods: We included derivation (n = 790) and validation (n = 565) cohorts from international tertiary centers. Patients underwent laboratory assessment and liver biopsy for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Based on 12 lipids, body mass index, aspartate aminotransferase, and alanine aminotransferase, the MASEF score was developed to identify at-risk MASH and compared to the FibroScan-AST (FAST) score. We further compared the performance of a FIB-4 + MASEF algorithm to that of FIB-4 + liver stiffness measurements (LSM) by vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE).
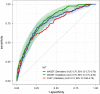
Results: The diagnostic performance of the MASEF score showed an area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of 0.76 (95% CI 0.72-0.79), 0.69, 0.74, 0.53, and 0.85 in the derivation cohort, and 0.79 (95% CI 0.75-0.83), 0.78, 0.65, 0.48, and 0.88 in the validation cohort, while FibroScan-AST performance in the validation cohort was 0.74 (95% CI 0.68-0.79; p = 0.064), 0.58, 0.79, 0.67, and 0.73, respectively. FIB-4+MASEF showed similar overall performance compared with FIB-4 + LSM by VCTE ( p = 0.69) to identify at-risk MASH.
Conclusion: MASEF is a promising diagnostic tool for the assessment of at-risk MASH. It could be used alternatively to LSM by VCTE in the algorithm that is currently recommended by several guidance publications.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Mazen Noureddin consults and received grants from Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Madrigal, Novo Nordisk, Takeda, and Terns. He consults, advises, and owns stock in Cytodyn. He consults and advises 89BIO, Altimmune, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, and Perspecturm. He has received grants and owns stock in Viking. He advises Blade, cohBar, EchoSens, Fractyl, Intercept, NorthSea, Pfizer, Siemens, and Roche Diagnostics. He has received grants from Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb, Conatus, Corcept, Enanta, Galmed, Galectin, Genfit, Madrigal, Novartis, Pfizer, Shire, and Zydus. He owns stock in Anaetos, ChronWell, Cima, and Rivus Pharma. Rebeca Mayo is employed by OWL Metabolomics. Ibon Martínez-Arranz is employed by OWL Metabolomics. Itziar Mincholé is employed by OWL Metabolomics. Jesus M. Banales consults and advises OWL Metabolomics. He consults and received grants from Albireo. He received grants and is on the speakers’ bureau for Incyte. He consults for CymaBay, Ikan Biotech, and QED Therapeutics. He is on the speakers’ bureau for Intercept. Kenneth Cusi consults and received grants from Novo Nordisk. He consults for Aligos, Allergan, Altimmune, Arrowhead, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Coherus, Covance, Eli Lilly, Fractyl, Genentech, Gilead, Hanmi, Intercept, Janssen, Madrigal, Pfizer, Prosciento, Sagimet, and Siemens. He received grants from Cirius, Echosens, Inventiva, LabCorp, National Institute of Health, Nordic Bioscience, Novartis, Poxel, and Zydus. Manuel Romero-Gómez advises and received grants from Gilead, Intercept, and Siemens. He consults for Galmed. He advises AbbVie, Alfa-Sigma, Madrigal, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. He received grants from Thera Therapeutics. Tatyana Kushner advises and received grants from Gilead. She consults for AbbVie. She advises Bausch and GlaxoSmithKline. Pablo Ortiz is employed by and owns stock in OWL Metabolomics. He is employed by Biosfer Teslab and Health in Code. Stephen A. Harrison consults, advises, is involved with trials, received grants, and owns stock in Akero, Galectin, GENFIT, Hepion, and NGM Bio. He consults, advises, is involved with trials, and received grants from Axcella, Gilead, Intercept, Madrigal, and Poxel. He consults, advises, received grants, and owns stock in NorthSea Therapeutics. He consults, advises, and is involved with trials for Terns. He consults, advises, and received grants from HighTide, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sagimet. He consults, advises, and owns stock in HistoIndex, Metacrine, and Sonic Incytes. He consults, received grants, and owns stock in Cirius. He consults, is involved with trials, and received grants from ENYO and Viking. He is involved with trials and received grants from Genentech. He consults and is involved with trials for Ionis. He consults and received grants from CiVi, CymaBay, Galmed, and Pfizer. He consults and owns stock in Hepta Bio. He consults and advises for Altimmune, Echosens North America, Foresite Labs, and Medpace. He advises and owns stock in ChronWell. He consults for AgomAb, Alentis, Aligos Therapeutics, Alimentiv, Blade, Bluejay, Boston Pharmaceuticals, Boxer Capital, Can-Fite BioPharma, the Chronic Liver Disease Foundation (CLDF), CohBar, Corcept, Fibronostics, Fortress Biotech, Galecto, Gelesis, Glaxo Smith Kline, GNS Healthcare, GRI Bio, Hepagene, Indalo, Inipharm, Innovate Biopharmaceuticals, Kowa Research Institute, Merck, MGGM, NeuroBo, Nutrasource, Perspectum, Piper Sandler, Prometic (now Liminal BioSciences), Ridgeline Therapeutics, Silverback, and Zafgen (now Larimar). He advises Arrowhead BVF Partners, Humana, and Pathai. He received grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Conatus, Immuron, and Second Genome. Quentin M. Anstee, on behalf of Newcastle University, consults and advises for Alimentiv, Akero, AstraZeneca, Axcella, 89Bio, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Galmed, GENFIT, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Hanmi, HistoIndex, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, IQVIA, Janssen, Madrigal, Medpace, Merck, NGM Bio, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, PathAI, Pfizer, Prosciento, Poxel, Resolution Therapeutics, Ridgeline Therapeutics, Roche, RTI, Shionogi, and Terns. He is on the speakers’ bureau for Fishawack, Integritas Communications, Kenes, Novo Nordisk, Madrigal, Medscape, and Springer Healthcare. He received grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Intercept. He holds intellectual property rights with Elsevier, Ltd. He serves as coordinator of the IMI2 LITMUS consortium. Arun J. Sanyal consults, advises, and received grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelhiem, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Fractyl, Gilead, Inventiva, Madrigal, Mallinckrodt, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. He consults and advises 89 Bio, Albrio, Alnylam, Amgen, Covance, Genetech, GenFit, Hemoshear, HistoIndex, Intercept, Jannsen, NGM Bio, Path AI, Poxel, Prosciento, Regeneron, Roche, Salix, Sequana, Terns, and Tiziana. He advises Akero, Axcella, Blade, Eisai, Hanmi, LG, Pharmanest, Pliant, Siemens, Takeda, Thera Technologies, Valeant, and Zealand Pharma. He received grants from Echosence-Sandhill, Galmed, Madrigal, Merck, Viking, and Zydus. He owns stock in Durect, Exhalenz, Galmed, GENFIT, Hemoshear, Rivis, Siemens, and Tiziana. He has other interests with Elsevier and UpToDate. The remaining authors (Emily Truong, Marco Arrese, María Teresa Arias-Loste, Radan Bruha, Paula Iruzubieta, Rocio Aller, Javier Ampuero, José Luis Calleja, Luis Ibañez-Samaniego, Patricia Aspichueta, Antonio Martín-Duce, Javier Crespo, and José M. Mato) have no conflicts to report.
Figures



References
-
- Rinella ME, Lazarus JV, Ratziu V, Francque SM, Sanyal AJ, Kanwal F, et al. . NAFLD Nomenclature consensus group. A multi-society Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology. 2023;78:1966–86. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, et al. . The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67:328–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

