Sources, Ionic Composition and Acidic Properties of Bulk and Wet Atmospheric Deposition in the Eastern Middle Adriatic Region
- PMID: 37505517
- PMCID: PMC10383331
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11070551
Sources, Ionic Composition and Acidic Properties of Bulk and Wet Atmospheric Deposition in the Eastern Middle Adriatic Region
Abstract
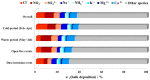
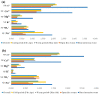
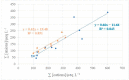
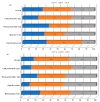
Atmospheric bulk and wet deposition samples were collected simultaneously at the background coastal site in the Eastern Middle Adriatic region in order to assess the impact of major ions (Cl-, NO3-, SO42-, Na+, K+, NH4+, Mg2+, Ca2+) on deposition acidity and distinguish the main sources. Higher ion levels were observed during the cold period, especially for Cl-, Na+, Mg2+ and K+. Dust intrusion caused significant increases in levels of Ca2+, Mg2+ and K+, while open-fire events increased the levels of K+. Deposition acidity showed seasonal differences as well as the influence of dust intrusion. Low ionic balance ratios indicated acidic deposition properties and the presence of organic anions. The highest neutralization ability was found for Ca2+, Na+ and NH4+. Several natural (marine, crustal) and anthropogenic sources were determined, as well as the formation of secondary aerosols. Wet deposition was characterized by higher contribution of sea salt fraction compared to bulk deposition and lower contribution of crustal fraction.
Keywords: deposited matter; dust intrusion; major ions; open-fire events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Chemical characterization of fine aerosols in respect to water-soluble ions at the eastern Middle Adriatic coast.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Apr;27(10):10249-10264. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07617-7. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31933087
-
Factors affecting the chemical composition of precipitation in Syria.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Aug;27(22):28408-28428. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08257-7. Epub 2020 May 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32418089
-
Spatial and long-term analysis of rainwater chemistry over the conterminous United States.Environ Res. 2020 Sep;188:109872. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109872. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 32846651
-
Chemical characterization of rainwater at a high-altitude site "Nainital" in the central Himalayas, India.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Feb;24(4):3959-3969. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8093-z. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 27913957
-
Atmospheric deposition of major ions and trace metals near an industrial area, Jordan.J Environ Monit. 2002 Dec;4(6):985-9. doi: 10.1039/b208697b. J Environ Monit. 2002. PMID: 12509055
References
-
- Morera-Gómez Y., Santamaría J.M., Elustondo D., Lasheras E., Alonso-Hernández C.M. Determination and Source Apportionment of Major and Trace Elements in Atmospheric Bulk Deposition in a Caribbean Rural Area. Atmos. Environ. 2019;202:93–104. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.01.019. - DOI
-
- Pereira J.N., Fornaro A., Vieira-Filho M. Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Deposition Species in an Agricultural Brazilian Region Using Positive Matrix Factorization. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021;8:12. doi: 10.3390/ecas2021-10698. - DOI
-
- Querol X., Pey J., Pandolfi M., Alastuey A., Cusack M., Pérez N., Moreno T., Viana M., Mihalopoulos N., Kallos G., et al. African Dust Contributions to Mean Ambient PM10 Mass-Levels across the Mediterranean Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2009;43:4266–4277. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.06.013. - DOI
-
- Pey J., Querol X., Alastuey A., Forastiere F., Stafoggia M. African Dust Outbreaks over the Mediterranean Basin during 2001–2011: PM10 Concentrations, Phenomenology and Trends, and Its Relation with Synoptic and Mesoscale Meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013;13:1395–1410. doi: 10.5194/acp-13-1395-2013. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

