Research Progress on Neurodevelopmental Toxicity in Offspring after Indirect Exposure to PFASs in Early Life
- PMID: 37505537
- PMCID: PMC10386615
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11070571
Research Progress on Neurodevelopmental Toxicity in Offspring after Indirect Exposure to PFASs in Early Life
Abstract
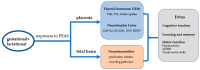
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are widespread environmental pollutants. There is increasing evidence that PFASs have various adverse health effects, including renal toxicity, metabolic dysfunction, endocrine disruption, and developmental toxicity. PFASs have been found to accumulate in the placenta, and some PFASs can cross the placental barrier and subsequently accumulate in the fetus via the maternal-fetal circulation. An increasing number of studies have shown that early life exposure to PFASs can affect fetal neurodevelopment. This paper reviews the characteristics of indirect exposure to PFASs in early life, the effects on neurodevelopment in offspring, and the possible mechanisms of toxic effects.
Keywords: PFAS; developmental neurotoxicity; early life exposure; placenta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances on neurodevelopment: Evidence-based risk assessment in the TRAEC strategy context.Environ Int. 2024 Sep;191:109003. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.109003. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 39276591
-
Concentrations of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human embryonic and fetal organs from first, second, and third trimester pregnancies.Environ Int. 2019 Mar;124:482-492. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Environ Int. 2019. PMID: 30684806
-
Insights into toxicological mechanisms of per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances by using omics-centered approaches.Environ Pollut. 2025 Feb 15;367:125634. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2025.125634. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Environ Pollut. 2025. PMID: 39755359 Review.
-
Developmental Exposures to Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): An Update of Associated Health Outcomes.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2018 Mar;5(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s40572-018-0173-4. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2018. PMID: 29556975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal and childhood exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and child cognition.Environ Int. 2018 Jun;115:358-369. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.03.025. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Environ Int. 2018. PMID: 29705692 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Developmental exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate(PFOS) impairs the endometrial receptivity.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 11;15(1):1747. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84732-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39799182 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Consequences of In Utero PFAS Exposure: Implications for Development and Long-Term Health.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Jun 10;22(6):917. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22060917. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40566344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Shadows of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): Unveiling the Impact of Perfluoroalkyl Substances on Ovarian Function, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Outcomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 10;26(14):6604. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146604. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hunting Metabolic Biomarkers for Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Review.Metabolites. 2024 Jul 19;14(7):392. doi: 10.3390/metabo14070392. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39057715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenatal and perinatal exposure to Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)-contaminated drinking water impacts offspring neurobehavior and development.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Mar 20;917:170459. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170459. Epub 2024 Jan 28. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38290673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blake B.E., Fenton S.E. Early Life Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Latent Health Outcomes: A Review Including the Placenta as a Target Tissue and Possible Driver of Peri- and Postnatal Effects. Toxicology. 2020;443:152565. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2020.152565. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ao J., Yuan T., Xia H., Ma Y., Shen Z., Shi R., Tian Y., Zhang J., Ding W., Gao L., et al. Characteristic and Human Exposure Risk Assessment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Study Based on Indoor Dust and Drinking Water in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019;254:112873. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sunderland E.M., Hu X.C., Dassuncao C., Tokranov A.K., Wagner C.C., Allen J.G. A Review of the Pathways of Human Exposure to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Present Understanding of Health Effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019;29:131–147. doi: 10.1038/s41370-018-0094-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi Y.J., Kim Lazcano R., Yousefi P., Trim H., Lee L.S. Perfluoroalkyl Acid Characterization in U.S. Municipal Organic Solid Waste Composts. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019;6:372–377. doi: 10.1021/acs.estlett.9b00280. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources