Screening of Toxic Effects of Neonicotinoid Insecticides with a Focus on Acetamiprid: A Review
- PMID: 37505564
- PMCID: PMC10383352
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11070598
Screening of Toxic Effects of Neonicotinoid Insecticides with a Focus on Acetamiprid: A Review
Abstract
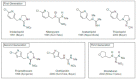
Recently, neonicotinoids have become the fastest-growing class of insecticides in conventional crop protection, with extensive usage against a wide range of sucking and chewing pests. Neonicotinoids are widely used due to their high toxicity to invertebrates, simplicity, flexibility with which they may be applied, and lengthy persistence, and their systemic nature ensures that they spread to all sections of the target crop. However, these properties raise the risk of environmental contaminations and potential toxicity to non-target organisms. Acetamiprid is a new generation insecticide, which is a safer alternative for controlling insect pests because of its low toxicity to honeybees. Acetamiprid is intended to target nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in insects, but its widespread usage has resulted in negative impacts on non-target animals such as mammals. This review summarizes in vivo and in vitro animal studies that investigated the toxicity of specific neonicotinoids. With summarized data, it can be presumed that certain concentrations of neonicotinoids in the reproductive system cause oxidative stress in the testis; spermatogenesis disruption; spermatozoa degradation; interruptions to endocrine function and Sertoli and Leydig cell function. In the female reproductive system, acetamiprid evokes pathomorphological alterations in follicles, along with metabolic changes in the ovaries.
Keywords: acetamiprid; neonicotinoids; reproduction; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neonicotinoids-from zero to hero in insecticide chemistry.Pest Manag Sci. 2008 Nov;64(11):1084-98. doi: 10.1002/ps.1631. Pest Manag Sci. 2008. PMID: 18712805 Review.
-
Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Apr 13;59(7):2897-908. doi: 10.1021/jf101303g. Epub 2010 Jun 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 20565065
-
The use of insecticide mixtures containing neonicotinoids as a strategy to limit insect pests: Efficiency and mode of action.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2022 Jun;184:105126. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2022.105126. Epub 2022 May 16. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35715064 Review.
-
Physiological Effects of Neonicotinoid Insecticides on Non-Target Aquatic Animals-An Updated Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 4;22(17):9591. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179591. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotoxicity assessment of sub-chronic oral administration of acetamiprid in Wistar rats.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2015;38(3):328-36. doi: 10.3109/01480545.2014.966382. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25308553
Cited by
-
Effect of formulations and adjuvants on the properties of acetamiprid solution and droplet deposition characteristics sprayed by UAV.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 2;15:1441193. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1441193. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39157513 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the acute sublethal effects of acetamiprid on honey bee neurological redox equilibrium.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 11;14(1):27514. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79274-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39528614 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into Olfactory Learning, Memory, and Mortality of Apis mellifera jemenitica after Exposure to Acetamiprid Insecticide.Insects. 2024 Jun 25;15(7):473. doi: 10.3390/insects15070473. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39057206 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Sex-Related Effects of Dietary Polyphenols and Metabolic Disruptors on Inflammatory and (Neuro) Endocrine Pathways in Obesity: The HEAL Project.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 23;16(21):3595. doi: 10.3390/nu16213595. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519428 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Diode Array Detector Method to Measure Seven Neonicotinoids in Wheat.Foods. 2024 Jul 16;13(14):2235. doi: 10.3390/foods13142235. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39063319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borpatragohain B., Sahoo S., Rai A. An Overview on the Impact, Interaction and Fate of Xenobiotic-Soil Organic Matter Complexes. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019;7:4935–4941.
-
- Aggrawal A. Agrochemical Poisoning. Forensic. Pathol. Rev. 2006;4:261–327. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59259-921-9_10. - DOI
-
- Garnett T., Wilkes A. Appetite for Change: Social, Economic and Environmental Transformations in China’s Food System. Food Climate Research Network 2014. [(accessed on 5 June 2023)]. Available online: http://www.ccjc-beijing.com/manage/images/2014619213033.pdf.
-
- FICCI . FICCI Knowledge Paper. FICCI; New Delhi, India: 2014. [(accessed on 14 March 2023)]. Safe & Judicious Use of Agrochemicals and Applications of Green Chemistry. Available online: https://ficci.in/spdocument/20377/agro-knowledge-paper.pdf.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

