Screening of Toxic Effects of Neonicotinoid Insecticides with a Focus on Acetamiprid: A Review
- PMID: 37505564
- PMCID: PMC10383352
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11070598
Screening of Toxic Effects of Neonicotinoid Insecticides with a Focus on Acetamiprid: A Review
Abstract
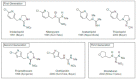
Recently, neonicotinoids have become the fastest-growing class of insecticides in conventional crop protection, with extensive usage against a wide range of sucking and chewing pests. Neonicotinoids are widely used due to their high toxicity to invertebrates, simplicity, flexibility with which they may be applied, and lengthy persistence, and their systemic nature ensures that they spread to all sections of the target crop. However, these properties raise the risk of environmental contaminations and potential toxicity to non-target organisms. Acetamiprid is a new generation insecticide, which is a safer alternative for controlling insect pests because of its low toxicity to honeybees. Acetamiprid is intended to target nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in insects, but its widespread usage has resulted in negative impacts on non-target animals such as mammals. This review summarizes in vivo and in vitro animal studies that investigated the toxicity of specific neonicotinoids. With summarized data, it can be presumed that certain concentrations of neonicotinoids in the reproductive system cause oxidative stress in the testis; spermatogenesis disruption; spermatozoa degradation; interruptions to endocrine function and Sertoli and Leydig cell function. In the female reproductive system, acetamiprid evokes pathomorphological alterations in follicles, along with metabolic changes in the ovaries.
Keywords: acetamiprid; neonicotinoids; reproduction; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Borpatragohain B., Sahoo S., Rai A. An Overview on the Impact, Interaction and Fate of Xenobiotic-Soil Organic Matter Complexes. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019;7:4935–4941.
-
- Aggrawal A. Agrochemical Poisoning. Forensic. Pathol. Rev. 2006;4:261–327. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59259-921-9_10. - DOI
-
- Garnett T., Wilkes A. Appetite for Change: Social, Economic and Environmental Transformations in China’s Food System. Food Climate Research Network 2014. [(accessed on 5 June 2023)]. Available online: http://www.ccjc-beijing.com/manage/images/2014619213033.pdf.
-
- FICCI . FICCI Knowledge Paper. FICCI; New Delhi, India: 2014. [(accessed on 14 March 2023)]. Safe & Judicious Use of Agrochemicals and Applications of Green Chemistry. Available online: https://ficci.in/spdocument/20377/agro-knowledge-paper.pdf.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

