Photocatalytic Degradation of Acetaminophen in Aqueous Environments: A Mini Review
- PMID: 37505569
- PMCID: PMC10386104
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11070604
Photocatalytic Degradation of Acetaminophen in Aqueous Environments: A Mini Review
Abstract
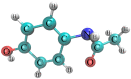
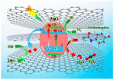
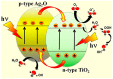
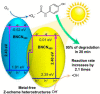
Over the past few decades, acetaminophen (ACT), a typical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), has gained global usage, positioning itself as one of the most extensively consumed medications. However, the incomplete metabolism of ACT leads to a substantial discharge into the environment, classifying it as an environmental contaminant with detrimental effects on non-target organisms. Various wastewater treatment technologies have been developed for ACT removal to mitigate its potential environmental risk. Particularly, photocatalytic technology has garnered significant attention as it exhibits high efficiency in oxidizing and degrading a wide range of organic pollutants. This comprehensive review aims to systematically examine and discuss the application of photocatalytic technology for the removal of ACT from aqueous environments. Additionally, the study provides a detailed overview of the limitations associated with the photocatalytic degradation of ACT in practical applications, along with effective strategies to address these challenges.
Keywords: acetaminophen; doping; heterojunction; photocatalyst; photocatalytic degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel organic assisted Ag-ZnO photocatalyst for atenolol and acetaminophen photocatalytic degradation under visible radiation: performance and reaction mechanism.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Aug;28(29):39637-39647. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13532-2. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33763832 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of parameters on the heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of pesticides and phenolic contaminants in wastewater: a short review.J Environ Manage. 2011 Mar;92(3):311-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.08.028. Epub 2010 Oct 14. J Environ Manage. 2011. PMID: 20950926 Review.
-
Recent Progress in Photocatalytic Degradation of Water Pollution by Bismuth Tungstate.Molecules. 2023 Dec 8;28(24):8011. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248011. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in architecturing the g-C3N4 based nanostructured photocatalysts: Synthesis, modifications and applications in water treatment.Chemosphere. 2022 Mar;291(Pt 1):132735. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132735. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34756947 Review.
-
A critical review on non-metal doped g-C3N4 based photocatalyst for organic pollutant remediation with sustainability assessment by life cycle analysis.Environ Res. 2024 Oct 1;258:119390. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119390. Epub 2024 Jun 13. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38879105 Review.
Cited by
-
Simulation and experimentation of iron-doped liquid metal-based gallium oxide photocatalysts for environmental applications harnessing solar energy.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 May;32(21):12913-12944. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36436-x. Epub 2025 May 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40338431 Free PMC article.
-
Facile electrochemical determination of acetaminophen at micromolar levels utilizing conjugated bimetallic Co-Zn porphyrin polymer electrodes as sensing platforms.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 23;15(26):21190-21198. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00178a. eCollection 2025 Jun 16. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40551840 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Characterization of a Novel Sol-Gel-Derived Ni-Doped TiO2 Photocatalyst for Rapid Visible Light-Driven Mineralization of Paracetamol.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;15(7):530. doi: 10.3390/nano15070530. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40214575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar M., Sridharan S., Sawarkar A.D., Shakeel A., Anerao P., Mannina G., Sharma P., Pandey A. Current research trends on emerging contaminants pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs): A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023;859:160031. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jiang L., Li Y., Chen Y., Yao B., Chen X., Yu Y., Yang J., Zhou Y. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the aquatic environment: Biotoxicity, determination and electrochemical treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2023;388:135923. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.135923. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

