A Comparable icELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive and Rapid Detection of 4,4'-Dinitrocarbanilide in Chicken
- PMID: 37505593
- PMCID: PMC10385411
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11070628
A Comparable icELISA and Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Sensitive and Rapid Detection of 4,4'-Dinitrocarbanilide in Chicken
Abstract
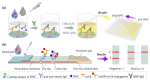
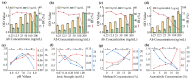
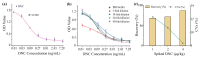
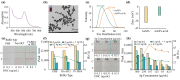
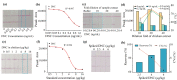
4,4'-dinitrocarbanilide (DNC) is a key component and marker residue of nicarbazin, which forms residues in edible tissue and then causes nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in humans if used excessively. To simplify sample preparation and monitor the DNC rapidly and accurately, a comparable icELISA and lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) was developed in this study. Briefly, the reaction parameters were explored for improving the sensitivity of icELISA and LFIA. Under the optimal conditions, methanol was selected as the extracting solvent for DNC in chicken, and 20- and 10-fold dilutions of sample extraction eliminated the matrix effect for icELISA and LFIA, separately. After sample pretreatment, the analysis properties of icELISA and LFIA were compared. The limit of detection of icELISA for DNC was 0.8 μg/kg, and the visual and quantitative limits of detection of LFIA were 8 and 2.5 μg/kg. Compared with icELISA, LFIA showed lower sensitivity but obvious advantages in terms of matrix tolerance and detection time (within 15 min). The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the developed assays satisfied the detection requirement even if using simple sample pretreatment. This comparable icELISA and LFIA provided mutual verifiability methods for the accurate detection of DNC in chicken.
Keywords: 4,4′-dinitrocarbanilide; chicken; icELISA; lateral flow immunoassay; rapid detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bampidis V., Bastos M.L., Christensen H., Dusemund B., Kouba M., Kos Durjava M., López-Alonso M., López Puente S., Marcon F., Mayo B., et al. Safety for the environment of Monimax® (monensin sodium and nicarbazin) for chickens for fattening, chickens reared for laying and for turkeys for fattening. EFSA J. 2019;17:e05888. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beier R.C., Stanker L.H. An antigen based on molecular modeling resulted in the development of a monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for the coccidiostat nicarbazin. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2001;444:61–67. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(01)01154-0. - DOI
-
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2010;15:1–72.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

